Overview
This article provides an insightful overview of warehouse operations, emphasizing the critical components and challenges associated with managing goods within a facility. It highlights the necessity of efficient processes, including:
- Receiving
- Storing
- Picking
- Packing
- Shipping
Furthermore, it addresses significant challenges such as:
- Labor shortages
- Stock precision
- Technology integration
These challenges can impede operational effectiveness. Understanding these elements is essential for Operations Managers aiming to optimize their warehouse strategies and overcome prevalent obstacles.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of warehouse operations is crucial in a world where efficiency and speed dictate market success. These operations, which encompass everything from receiving and storing to packing and shipping, form the backbone of effective supply chain management.
As businesses strive to meet the rising expectations of consumers for rapid delivery, they encounter significant challenges, including:
- Labor shortages
- Technology integration issues
How can companies navigate these complexities to optimize their warehouse processes and enhance overall productivity? Addressing these challenges is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market.
Define Warehouse Operations and Their Importance
The operations in a warehouse encompass a range of essential processes for managing goods within a facility, including:
- Receiving
- Storing
- Picking
- Packing
- Shipping products
The significance of cannot be overstated, as they directly influence a firm’s ability to meet customer demands and manage inventory efficiently. In today’s market, where over half of consumers aged 18-34 anticipate same-day delivery, and more than 60% are willing to pay a premium for it, optimizing these operations is imperative for ensuring timely deliveries and reducing operational costs.
Furthermore, proficient warehouse management bolsters overall supply chain efficiency, which is crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage. For instance, adopting streamlined receiving practices not only minimizes stock errors but also results in substantial cost savings through optimized labor and resource allocation. Accurate receiving methods are vital for preserving precise stock records, while comprehensive staff training on equipment operation ensures workforce proficiency.
Moreover, recognizing the risks associated with warehousing, such as natural disasters, and implementing stringent quality control measures during receiving are essential for sustaining inventory quality. As companies strive to enhance their logistics, understanding and optimizing operations in a warehouse become key strategies for achieving operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Explore Key Components of Warehouse Operations
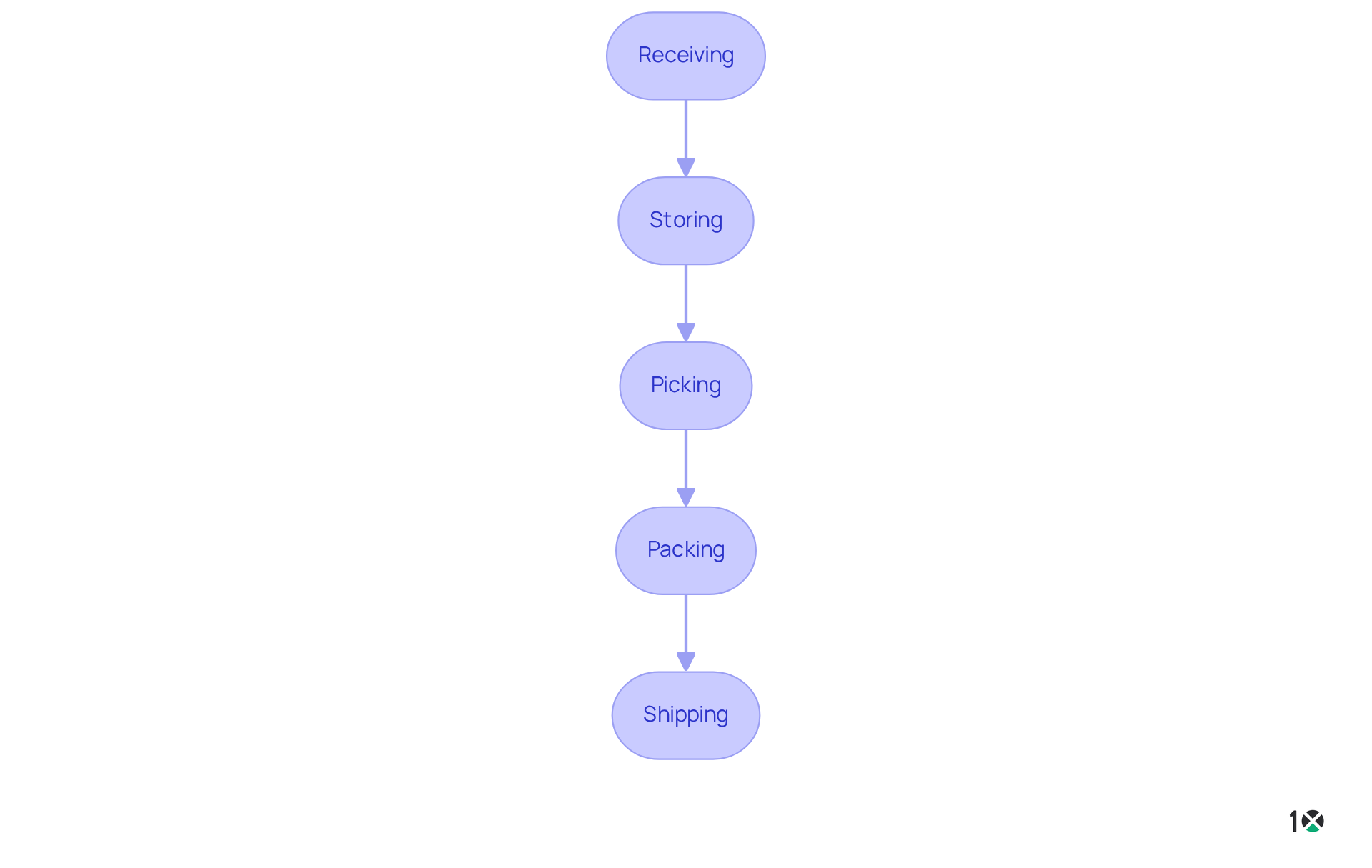
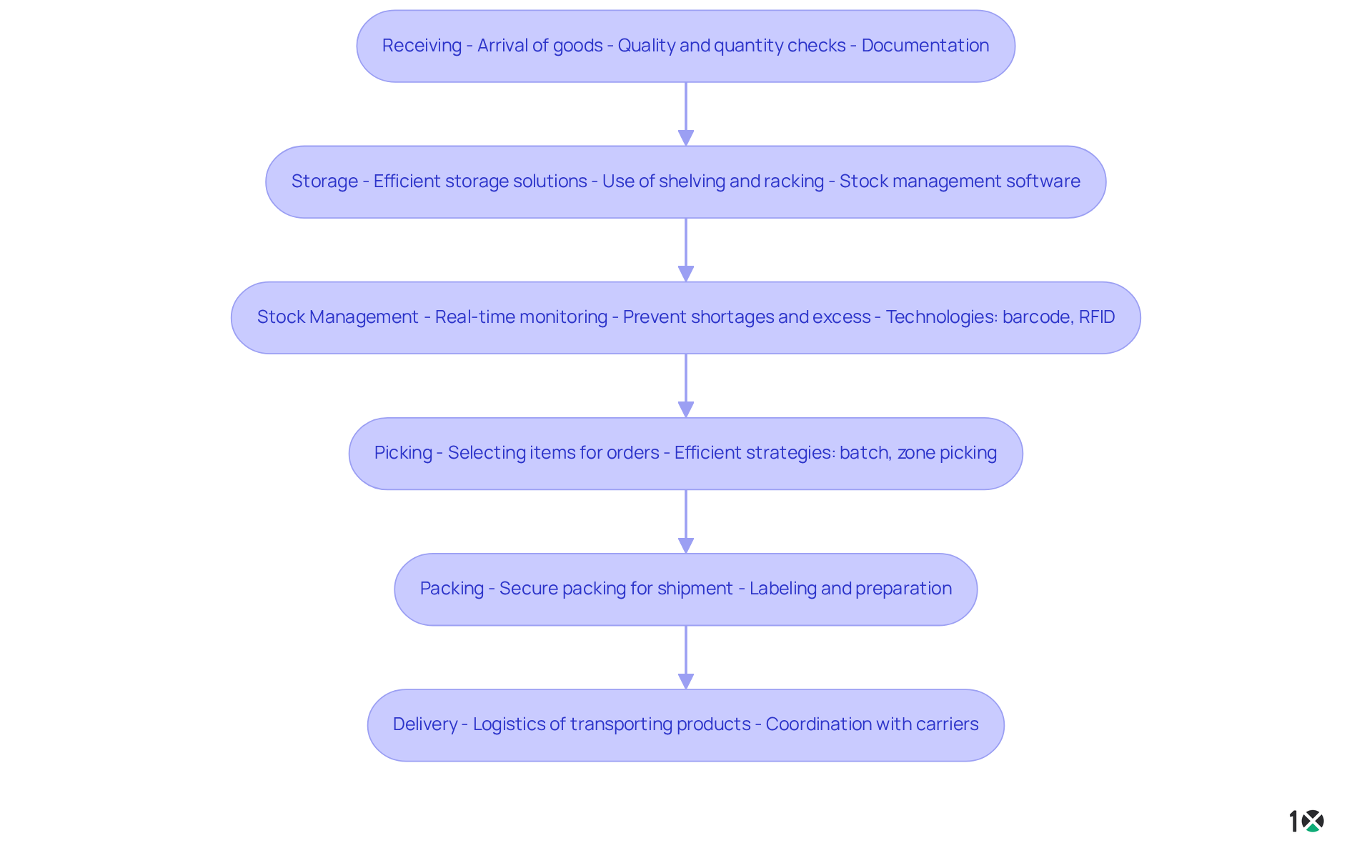
The efficiency and effectiveness of operations in a warehouse depend on key components.
- Receiving: This initial step marks the arrival of goods at the warehouse. Implementing appropriate receiving procedures ensures that items are thoroughly examined for quality and quantity, and accurately documented in the stock system.
- Storage: Efficient storage solutions are vital for maximizing space and ensuring easy access to products. This includes the strategic use of shelving, racking systems, and stock management software.
- Stock Management: Real-time monitoring of stock levels is essential for preventing shortages and excess inventory. Technologies such as barcode scanning and RFID systems significantly enhance inventory accuracy.
- Picking: This process involves selecting items from storage to fulfill customer orders. Employing efficient picking strategies, such as batch picking or zone picking, can drastically reduce order fulfillment times.
- Packing: After items are picked, they must be securely packed for shipment. This step typically involves for transport.
- Delivery: The final phase in storage processes, shipping encompasses the logistics of transporting products to clients. This includes coordinating with carriers and ensuring timely deliveries.
By understanding these elements, companies can identify areas for improvement in their operations in a warehouse and implement strategies to enhance their storage processes.
Identify Challenges in Warehouse Operations
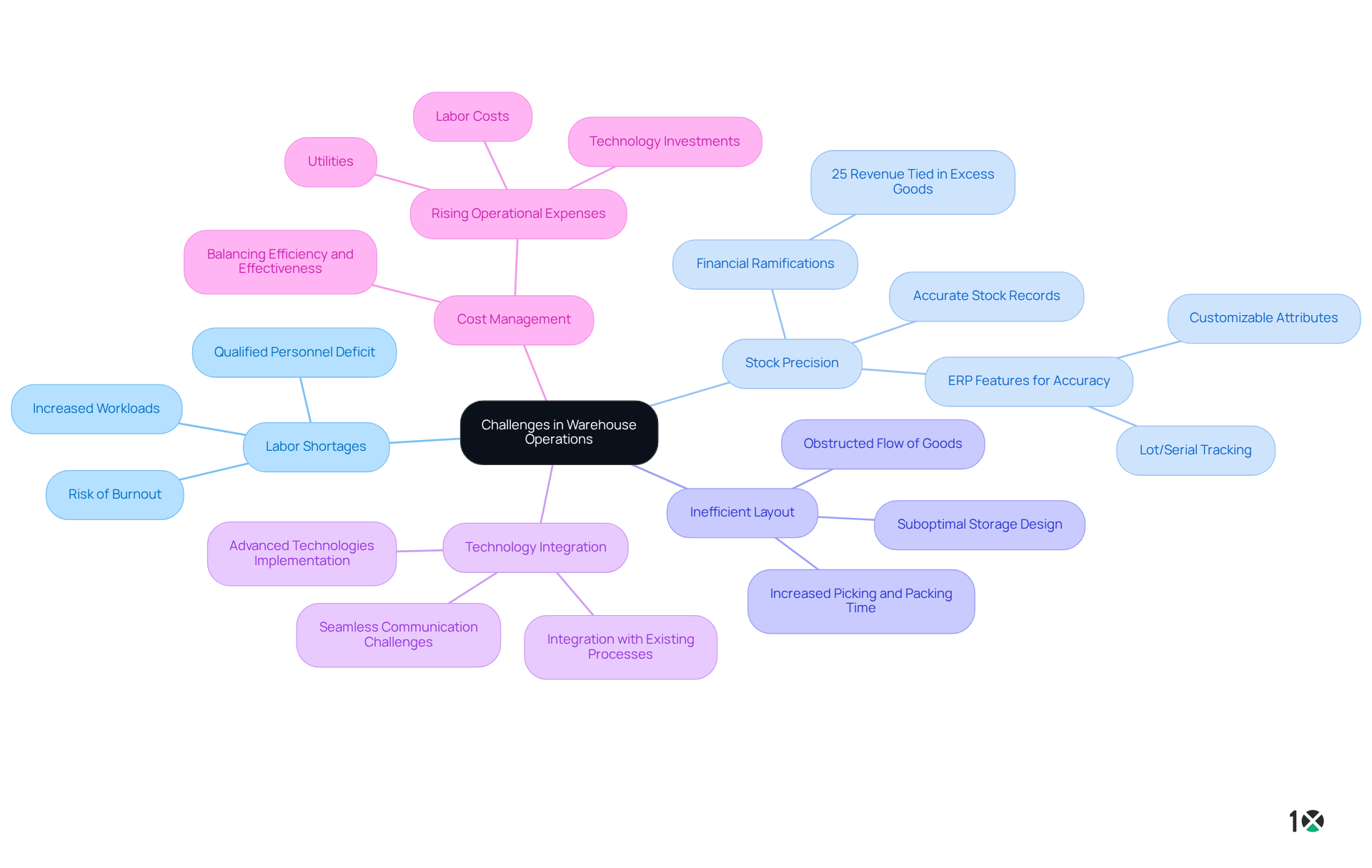
The challenges faced by operations in a warehouse significantly hinder efficiency and productivity. Key issues include:
- Labor Shortages: The logistics industry is grappling with a notable shortage of qualified personnel, complicating staffing in storage facilities. This deficit can lead to , elevating the risk of burnout and diminishing overall operational efficiency. As Vince Lombardi aptly noted, individual commitment to a group effort is essential for teamwork—an element crucial in overcoming labor shortages.
- Stock Precision: Accurate stock records are vital for effective warehouse management. Discrepancies can lead to stockouts or overstocking, ultimately resulting in customer dissatisfaction. Statistics reveal that poor stock accuracy can tie up to 25% of a company’s revenue in excess goods, highlighting the financial ramifications of this issue. Leveraging features such as customizable attributes and lot/serial tracking in 10X ERP can significantly enhance inventory accuracy and visibility.
- Inefficient Layout: A suboptimal storage design can obstruct the flow of goods, extending the time required for picking and packing. Optimizing the layout is essential for boosting operational performance and reducing labor costs associated with operations in a warehouse.
- Technology Integration: As storage facilities increasingly implement advanced technologies, integrating these systems with existing processes poses challenges. Ensuring seamless communication between various software solutions, such as inventory management software and barcode systems, is critical for maximizing efficiency and minimizing disruptions.
- Cost Management: Rising operational expenses, including labor, utilities, and technology investments, exert pressure on storage budgets. Warehouse managers must consistently explore avenues to reduce costs while upholding high service levels, striking a balance between efficiency and effectiveness.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive approach, which includes investments in employee training, the adoption of advanced technologies, and regular evaluations of operational processes, particularly operations in a warehouse, to identify areas for improvement. By cultivating a culture of continuous improvement, warehouses can enhance their operational capabilities and better meet customer demands.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of warehouse operations is crucial for any business aiming to thrive in a competitive market. Effective management of warehouse processes—from receiving to shipping—is not merely operational; it is a strategic necessity. Optimizing these operations can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency, ultimately leading to a stronger market position.
Key components such as:
- Receiving
- Storage
- Stock management
- Picking
- Packing
- Delivery
are vital to the overall functionality of a warehouse. Each stage plays a significant role in ensuring that goods are handled efficiently and accurately. However, challenges like:
- Labor shortages
- Stock precision issues
- Inefficient layouts
- Technology integration hurdles
- Rising costs
can impede these operations. Addressing these challenges through proactive measures—such as investing in employee training and advanced technologies—is essential for maintaining high service levels and operational excellence.
The significance of warehouse operations extends beyond mere logistics; it is a fundamental element of a successful supply chain strategy. Businesses must recognize the impact of well-optimized warehouse processes on their overall efficiency and customer satisfaction. By embracing a culture of continuous improvement and actively seeking solutions to common operational challenges, companies can not only enhance their warehouse capabilities but also position themselves for long-term success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are warehouse operations?
Warehouse operations refer to the essential processes involved in managing goods within a facility, which include receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping products.
Why are warehouse operations important?
Effective warehouse operations are crucial as they directly impact a company’s ability to meet customer demands and manage inventory efficiently, which is vital in today’s market where timely deliveries are expected.
How does optimizing warehouse operations affect customer satisfaction?
Optimizing warehouse operations ensures timely deliveries, which enhances customer satisfaction, especially as a significant percentage of consumers expect same-day delivery and are willing to pay extra for it.
What role does warehouse management play in supply chain efficiency?
Proficient warehouse management improves overall supply chain efficiency, helping companies maintain a competitive advantage by minimizing stock errors and optimizing labor and resource allocation.
What are some best practices for receiving goods in a warehouse?
Best practices for receiving goods include adopting streamlined receiving methods, ensuring accurate stock records, and providing comprehensive staff training on equipment operation.
What risks are associated with warehousing?
Risks associated with warehousing include natural disasters and potential inventory quality issues, which necessitate the implementation of stringent quality control measures during the receiving process.
How does warehouse management contribute to operational excellence?
By understanding and optimizing warehouse operations, companies can achieve operational excellence, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction, which are key strategies in improving logistics.
