Overview
This article centers on the essential seven ERP acronyms that every operations manager must know, highlighting their critical role in managing business processes. Each acronym, including CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and WMS (Warehouse Management System), significantly contributes to enhancing operational efficiency, data accuracy, and overall business performance. Understanding these concepts is not merely beneficial; it is essential for effective decision-making in today’s competitive landscape. Operations managers are urged to familiarize themselves with these acronyms to navigate their challenges more effectively and drive organizational success.
Introduction
In an increasingly complex business landscape, the acronyms associated with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) have become essential knowledge for operations managers. Understanding these key terms not only facilitates smoother operations but also empowers organizations to leverage technology for enhanced efficiency and decision-making. However, with the rapid evolution of ERP systems and the integration of various technologies, what are the most critical acronyms that every operations manager should be familiar with to stay competitive? This article delves into seven pivotal ERP acronyms that can transform operational strategies and drive business success.
10X ERP: Cloud-Based Enterprise Resource Planning
10X ERP stands out as an innovative cloud-based software specifically designed for growing distributors, showcasing the importance of the ERP acronym in Enterprise Resource Planning. Its modern, user-friendly interface is accessible from any web browser, empowering businesses to manage operations efficiently from any location. A key feature of the platform is its real-time data processing capabilities, providing users with immediate access to critical information. This immediacy is essential for making informed decisions in the fast-paced distribution landscape, where can significantly enhance operational efficiency and client satisfaction.
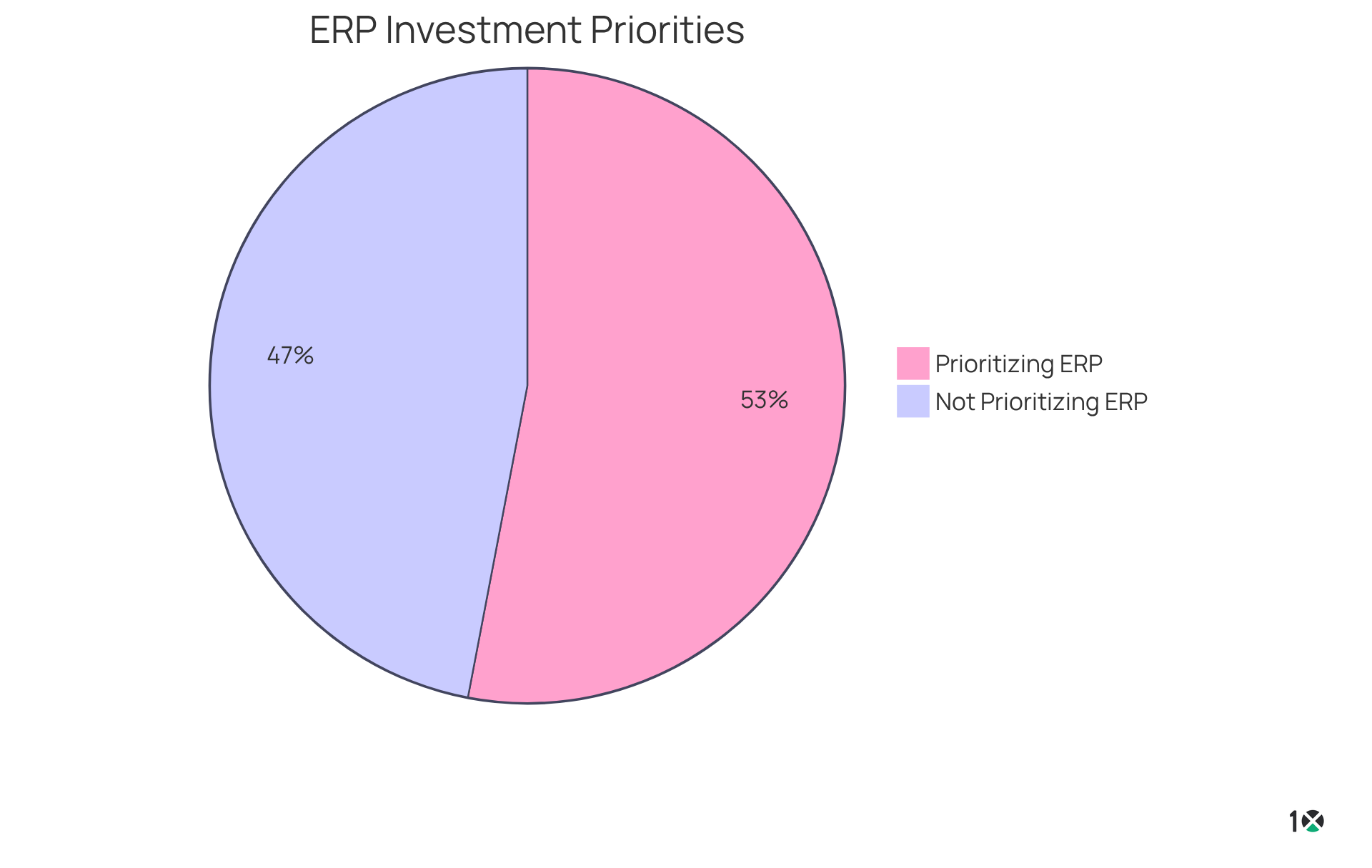
Recent trends reveal a growing adoption of cloud solutions that utilize the ERP acronym, driven by their flexibility and scalability. In fact, 53% of businesses are prioritizing the ERP acronym as a key investment. The global cloud ERP market was valued at USD 34.83 billion in 2023, with projections indicating it will reach USD 110.26 billion by 2030, highlighting a robust growth trajectory. The integration of real-time information processing not only enhances decision-making but also streamlines operations, enabling distributors to respond swiftly to market changes and customer demands.
As organizations increasingly embrace digital transformation, the benefits of cloud ERP solutions—such as improved information accuracy and operational efficiency—become increasingly clear. These tools are essential for modern distribution management, offering the capabilities necessary to thrive in a competitive environment.
ERP: Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning
The ERP acronym represents a pivotal advancement in the integrated management of core business processes, driven by sophisticated software and technology. By unifying data across various departments—such as finance, human resources, and supply chain—an ERP solution not only streamlines operations but also enhances visibility throughout the organization. This integration not only boosts efficiency but also equips decision-makers with real-time insights, facilitating more effective resource allocation.
Current trends reveal that:
- 92% of wholesalers and distributors leverage ERP software, which underscores the [importance of the ERP acronym in the industry](https://thecfoclub.com/operational-finance/erp-statistics).
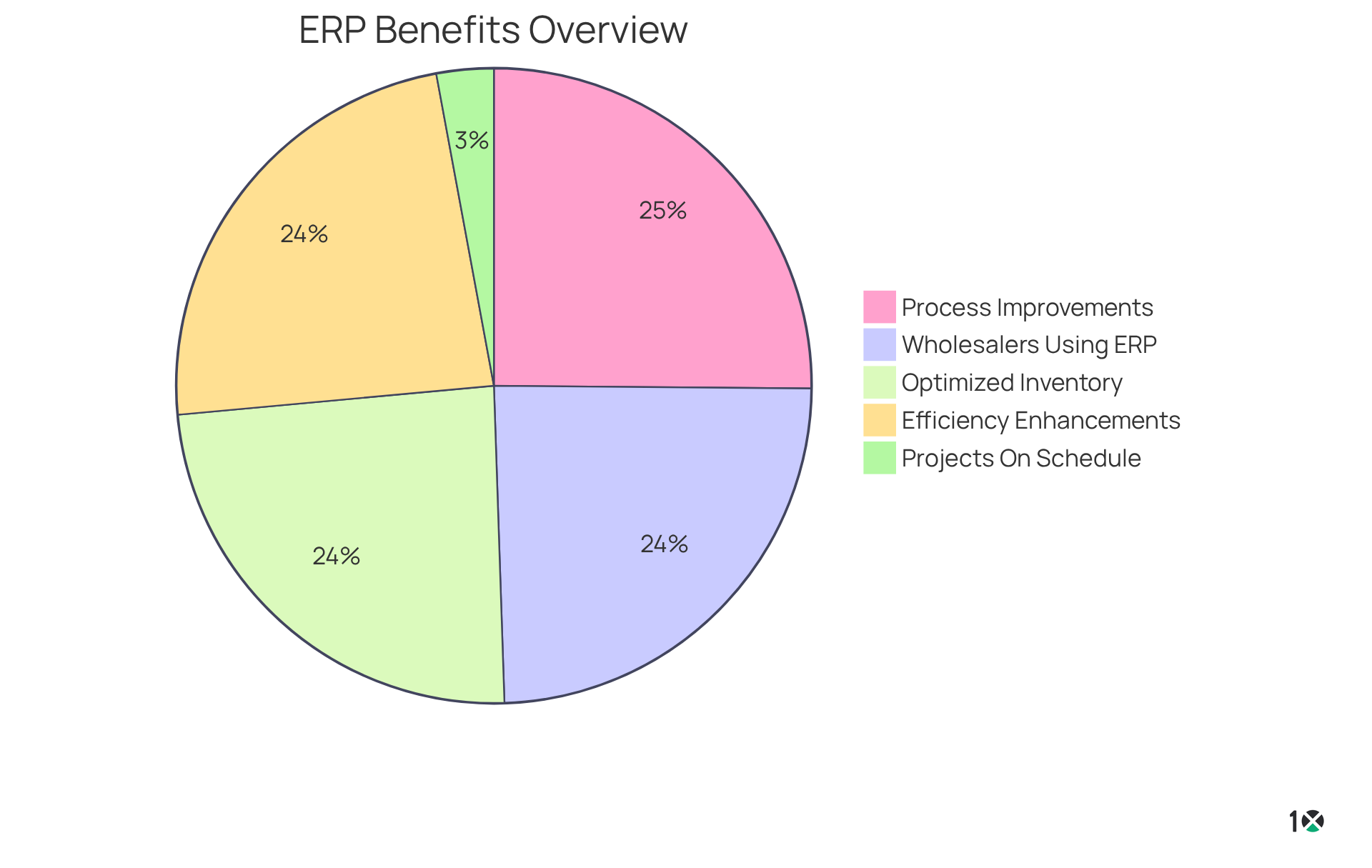
- As businesses increasingly adopt cloud-based solutions, known by the ERP acronym, they report significant enhancements in operational efficiency; indeed, 95% of companies experience process improvements following implementation.
- Furthermore, 89% of ERP users cite efficiency enhancements as a primary benefit, highlighting the transformative potential of these solutions.
Experts emphasize the importance of the ERP acronym in business process integration, indicating that organizations utilizing these systems can achieve optimized inventory levels—91% of companies report this outcome. As Cem Dilmegani articulates, “The top three advantages that companies reported they obtained from an ERP solution are reduced process time, enhanced collaboration, and a centralized information framework.”
Approaching 2025, the demand for ERP solutions, commonly referred to by the ERP acronym, continues to surge, driven by the need for seamless information integration and enhanced operational capabilities. With 71% of businesses aiming to harness ERP data for , the relevance of the ERP acronym in modern enterprises is more pronounced than ever. It is also crucial to recognize that only 11% of ERP projects go live as scheduled, illustrating the challenges organizations encounter during implementation.
CRM: Customer Relationship Management Explained
Client Relationship Management (CRM) platforms serve as essential resources for managing a business’s interactions with both existing and prospective clients. By leveraging analytical insights from client history, CRMs significantly enhance business relationships, streamline processes, and boost profitability. When combined with ERP platforms, the ERP acronym provides a comprehensive view of client interactions, which is crucial for delivering outstanding service and identifying new sales opportunities.
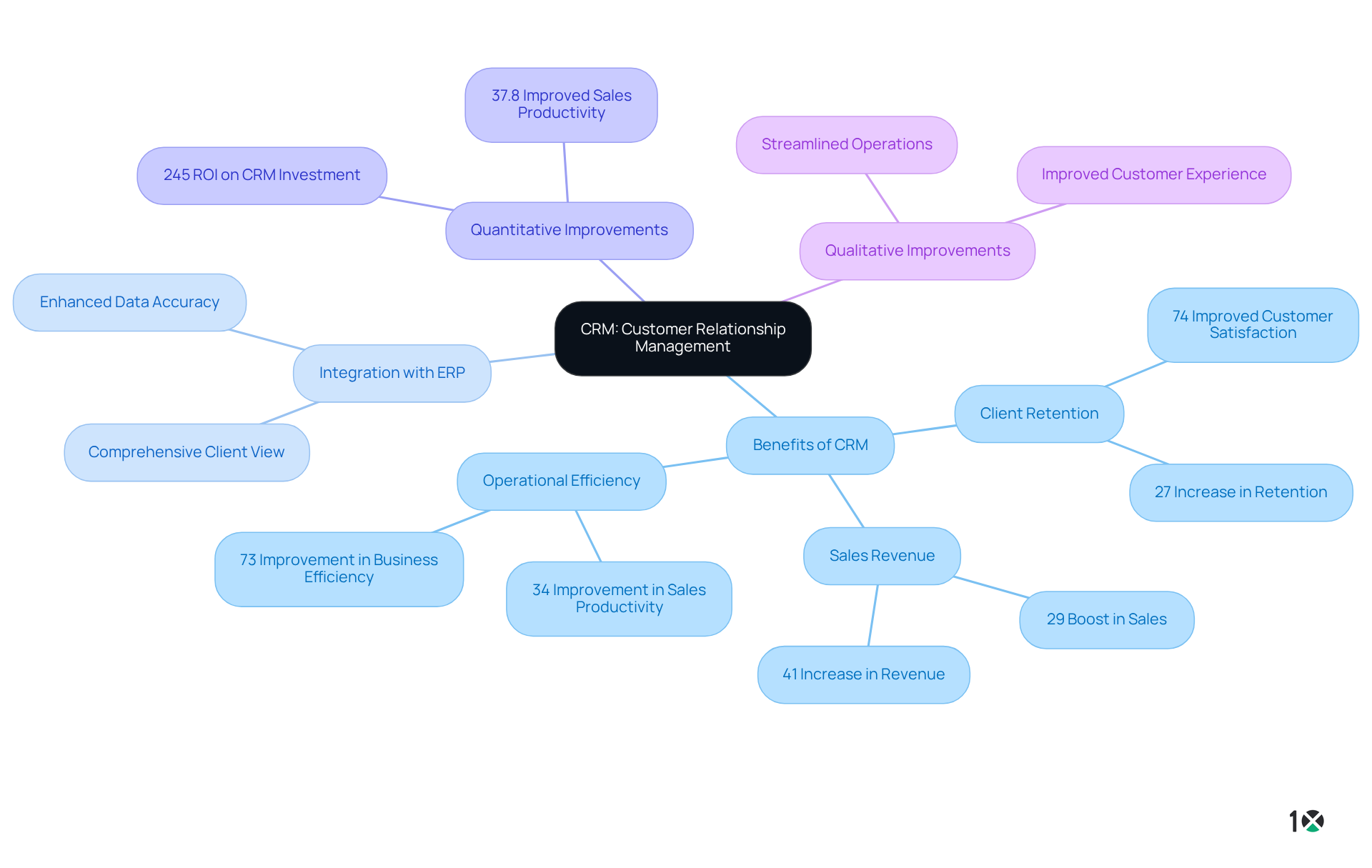
The integration of CRM with ERP solutions, known by the ERP acronym, not only improves data accuracy but also elevates client retention rates. Companies that embrace this integration often report a 27% increase in client retention, while 47% of firms assert that CRM software plays a critical role in enhancing client retention. This underscores the effectiveness of a unified approach to client management. Moreover, organizations utilizing CRM tools experience a 41% increase in sales revenue, along with a 29% rise in sales and a 34% improvement in sales productivity, highlighting the financial advantages of these systems.
Successful examples abound in the distribution sector, where firms have seen remarkable improvements in client relationships through the integration of CRM and the ERP acronym. For instance, companies that fully adopt CRM solutions report an 87% enhancement in sales performance, illustrating the transformative impact of these technologies on operational efficiency and client satisfaction.
Experts emphasize that merging CRM with systems defined by the ERP acronym transcends mere technical enhancement; it represents a strategic decision that fosters collaboration across departments, ultimately leading to improved client experiences. As Michael Scheiner notes, “CRM, or Customer Relationship Management, is more than just a tool for managing contacts—it drives sales, streamlines operations, and boosts customer satisfaction.” With the by 2029, the significance of this integration will only grow, making it an essential consideration for operations managers seeking to drive business success.
PIM: Product Information Management Overview
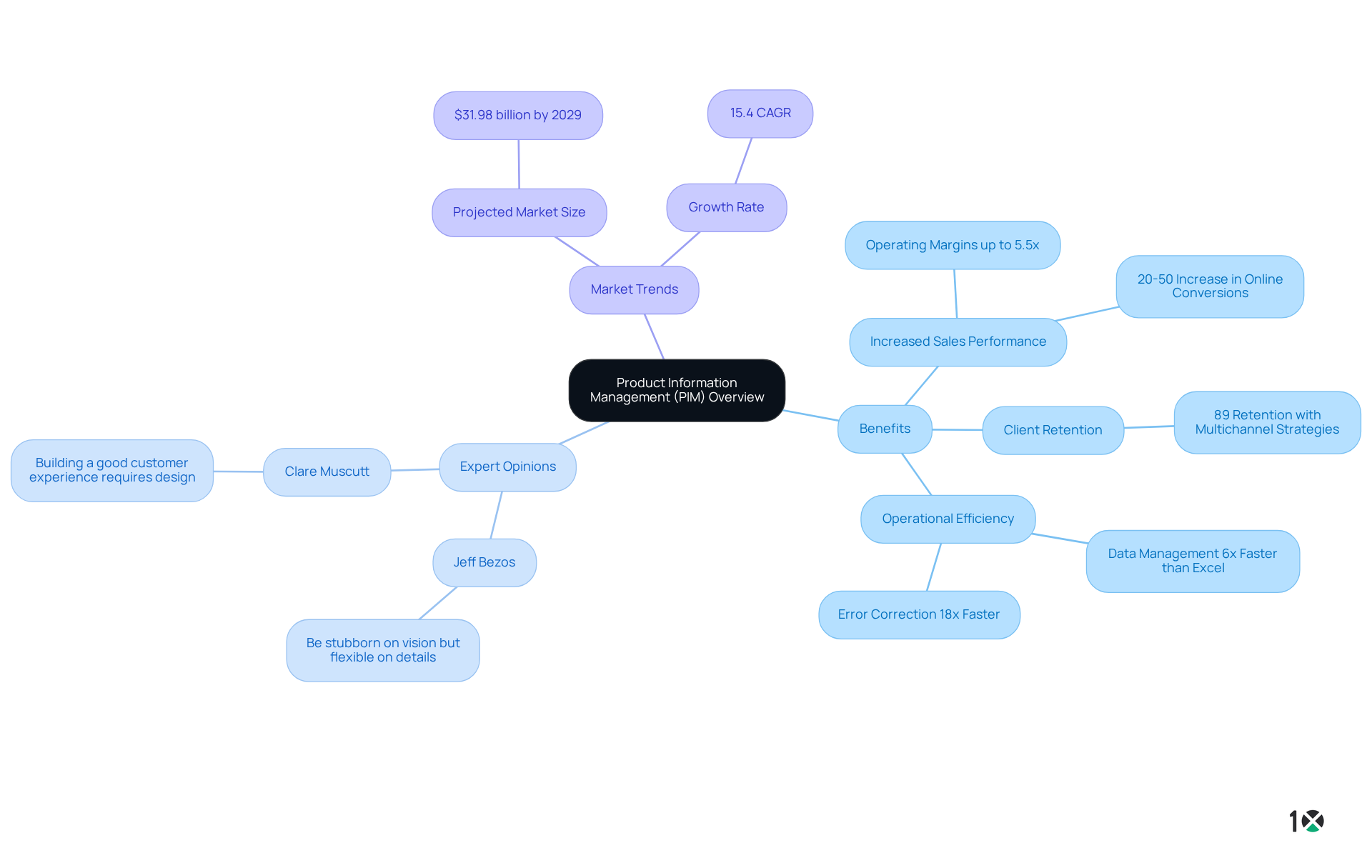
Product Information Management (PIM) encompasses the essential processes and tools designed to oversee product information across multiple channels. By centralizing this information, PIM systems guarantee consistency and accuracy—critical factors for distributors. Accurate product information can significantly enhance sales performance; organizations utilizing PIM may achieve operating margins up to 5.5 times greater than those relying on traditional methods. Furthermore, companies adopting integrated multichannel strategies retain as much as 89% of their clients, underscoring the importance of efficient product information management.
Industry leaders stress the imperative of effective product data management. Jeff Bezos articulates the necessity of being ‘stubborn on vision but flexible on details,’ a philosophy that resonates with the adaptability required in PIM frameworks. Similarly, Clare Muscutt asserts that ‘building a good customer experience does not happen by accident; it happens by design,’ reinforcing that accurate product information is foundational to customer satisfaction.
PIM systems are pivotal in ensuring the accuracy of product information. They streamline information management processes, allowing corrections to be made up to 18 times faster than conventional techniques. This efficiency is particularly advantageous for distributors, who frequently encounter challenges in maintaining accurate product information across diverse sales channels. Recent innovations in PIM solutions, including the , further enhance information accuracy and operational efficiency.
Examples of successful PIM implementation illustrate its impact on product information management. Companies that have adopted PIM solutions report improved accuracy and consistency in their product information, resulting in enhanced customer experiences and increased sales. Additionally, businesses prioritizing product data quality see an average reduction of 25% in product returns, highlighting the financial benefits of effective PIM solutions. As the global PIM market is projected to reach $31.98 billion by 2029, with an annual growth rate of 15.4%, the significance of effective product information management for distributors is undeniable.
For operations managers, implementing a robust PIM solution is not just a strategic advantage; it is a necessity for thriving in a competitive market.
WMS: Warehouse Management System Insights
(WMS) are essential software solutions that effectively manage and optimize warehouse operations. They provide functionalities such as real-time inventory tracking, streamlined order fulfillment, and efficient shipping logistics. By integrating WMS with solutions that utilize the ERP acronym, visibility into inventory levels is significantly enhanced, enabling distributors to reduce errors and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
The impact of WMS on inventory precision is profound; companies utilizing these solutions can achieve a 99% improvement in inventory accuracy, which minimizes picking mistakes and ensures timely deliveries. Additionally, WMS can result in a 10-50% increase in productivity by eliminating time wasted searching for items, thus enhancing order fulfillment processes. Notably, employing integrated order processing can boost productivity by 25%, underscoring the efficiency gains from WMS integration with ERP platforms.
Logistics specialists emphasize the importance of merging WMS with ERP solutions, noting that this combination, related to the ERP acronym, fosters improved data synchronization and operational clarity. As Wael Safwat aptly stated, ‘It’s not the organizations that are competing. It’s the supply chains that are competing.’ This underscores the necessity for distributors to adopt advanced technologies like WMS to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Successful case studies of warehouse management optimization highlight the advantages of using the ERP acronym in this integration. For example, companies that have implemented WMS alongside ERP have reported significant reductions in labor costs—by as much as 10-45%—through automation and optimized picking routes. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also boosts customer satisfaction by ensuring accurate and timely order fulfillment.
In conclusion, WMS plays a pivotal role in optimizing warehouse operations, driving improvements in inventory accuracy and order fulfillment, and ultimately contributing to a more efficient supply chain. The warehouse management market is projected to grow from $4.16 billion in 2019 to $7.90 billion by 2027, emphasizing the increasing significance of these solutions, which are currently utilized in 85% of warehouse operations.
MRP: Material Requirements Planning Basics
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) serves as a vital framework for production planning, scheduling, and inventory control, specifically designed to optimize manufacturing processes. By determining the quantity and timing of material requirements, MRP ensures that the right materials are available for production, effectively preventing overstocking. When integrated with ERP platforms, the ERP acronym significantly enhances coordination between production and inventory management.
However, the implementation of MRP is not without its challenges. Organizations often face difficulties related to information precision, the complexity of the framework, and the necessity for ongoing updates. Navigating these hurdles is essential for organizations aiming to fully leverage the capabilities of MRP.
The role of MRP frameworks in improving inventory management cannot be overstated. By utilizing real-time information and analytics, manufacturers can accurately forecast future product demand based on historical data and market trends. This alignment ensures that production schedules meet customer needs effectively. A notable example is a renowned restaurant chain that successfully implemented MRP to synchronize procurement, production, and inventory management, leading to reduced waste and enhanced supply chain responsiveness.
Experts emphasize the importance of integrating MRP with ERP frameworks, highlighting that ERP is an acronym for Enterprise Resource Planning. Mark Thompson, a Senior Operations Manager at a Global F&B Corporation, asserts that advanced MRP solutions empower businesses to respond swiftly to changing consumer preferences and market trends. Dr. Laura Reynolds, a Supply Chain Consultant, echoes this sentiment, highlighting MRP’s critical role in optimizing inventory levels and aligning production activities with market demands.
Successful instances of MRP enhancing production planning are evident across various industries. The automotive sector, for example, has effectively utilized MRP to streamline production lines, ensuring the timely availability of components while enhancing overall operational efficiency. Similarly, the electronics industry has reaped the benefits of MRP’s advanced demand forecasting and inventory management capabilities. By integrating MRP with ERP platforms, organizations can achieve a unified framework that not only improves production planning but also fosters cost-effectiveness and resource optimization, which is essential in the context of the ERP acronym.
To maximize the benefits of MRP, operations managers should consider implementing complementary solutions such as Available to Promise (ATP), which can significantly . Furthermore, investing in training and development for staff is crucial to overcoming implementation challenges and ensuring the effective utilization of MRP tools.
SCM: Supply Chain Management Fundamentals
(SCM) is crucial for overseeing the flow of goods and services, encompassing all processes that transform raw materials into finished products. It requires meticulous planning and management of activities related to sourcing, procurement, conversion, and logistics. By integrating SCM with ERP acronym platforms, organizations can achieve enhanced coordination and efficiency throughout the supply chain. This integration not only streamlines operations but also significantly reduces costs—companies that effectively manage their supply chains can decrease logistics costs by up to 15% and improve service efficiency by 65%.
Moreover, effective SCM fosters better customer satisfaction, as timely and accurate fulfillment is essential. Studies indicate that 65% of customers abandon retailers after just two to three late deliveries. As supply chain specialists emphasize, a well-integrated SCM and ERP acronym framework is vital for achieving operational excellence and maintaining a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic market. Organizations must prioritize this integration to not only meet but exceed customer expectations.
BI: Business Intelligence in ERP Systems
Business Intelligence (BI) represents the technologies and strategies that enterprises utilize to analyze business information effectively. Within the context of ERP systems, the ERP acronym highlights the crucial role of in synthesizing data from various sources, yielding insights that drive strategic decision-making. By leveraging BI, operations managers can identify trends, anticipate demand, and refine processes based on actionable insights. Notably, organizations that employ ERP analytics have experienced significant improvements in operational efficiency. For instance, one case study illustrates how actionable reporting transformed conventional information into digestible formats, empowering stakeholders to tackle business challenges effectively.
Moreover, organizations that harness real-time market insights through BI tools can proactively adapt to economic fluctuations, thereby maintaining a competitive edge. Industry experts assert that integrating BI into operations management not only enhances decision-making but also cultivates a culture of data-driven growth. This ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction and profitability, making BI an essential component for organizations aiming to thrive in a dynamic market.
API: Application Programming Interface in ERP
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are essential protocols that facilitate effective communication among diverse software applications. The ERP acronym highlights how APIs within ERP platforms enable seamless integration with various software solutions, significantly enhancing functionality and information-sharing capabilities. For operations managers, a comprehensive understanding of APIs is crucial for optimizing workflows and ensuring cohesive performance across platforms.
The integration of APIs can automate critical tasks such as:
- Data entry
- Invoicing
- Inventory tracking
This minimizes human error and allows staff to focus on higher-value activities. This automation is particularly advantageous in distribution, where is vital for maintaining a competitive edge.
Recent statistics reveal that approximately 60% of API users report infrequent malfunctions, highlighting the reliability of well-implemented APIs. This reliability is essential for operational efficiency in distribution, ensuring that processes run smoothly without interruptions. Furthermore, the API management market is projected to expand at a CAGR of 32.9%, reflecting the growing importance of APIs in contemporary business environments and their role in enhancing ERP solutions.
Successful instances of API optimization in workflows include the integration of systems defined by the ERP acronym and CRM, which offers a unified view of operations, enhances cash flow management, and improves customer experiences. By consolidating information into a single reliable source, organizations can respond swiftly to demand fluctuations and prevent excess inventory that could hinder cash flow.
As businesses continue to evolve, staying updated on the latest API developments is imperative. The ability to leverage APIs effectively can yield substantial operational enhancements, making them a critical component of any modern ERP acronym strategy.
IoT: Internet of Things and ERP Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents a transformative interconnected system of physical devices that not only gather but also share vital information. In the realm of ERP systems, often referred to by the ERP acronym, the integration of IoT can significantly enhance information collection, providing real-time insights into operational efficiency.
By leveraging IoT within the frameworks of the ERP acronym, organizations can achieve:
- Improved monitoring capabilities
- Automation of critical processes
- Informed decisions driven by real-time data sourced from connected devices
This integration is not merely an upgrade; it is a for organizations aiming to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Conclusion
The exploration of key ERP acronyms reveals their critical role in modern operations management, emphasizing the necessity for businesses to understand and leverage these systems. The integration of various ERP components—ranging from cloud-based solutions to business intelligence tools—equips organizations with the agility and insights required to thrive in competitive markets.
Throughout this discussion, significant insights have emerged, including the transformative benefits of cloud ERP systems, the importance of customer relationship management (CRM) in enhancing client interactions, and the vital role of product information management (PIM) in ensuring data accuracy. The synergy between warehouse management systems (WMS), material requirements planning (MRP), supply chain management (SCM), and APIs further illustrates how these acronyms work together to optimize operations. As organizations increasingly adopt these technologies, the potential for improved efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall business performance becomes evident.
In light of rapid advancements in technology, operations managers are encouraged to prioritize the integration of these ERP systems into their strategies. By doing so, they can harness the power of real-time data, streamline processes, and ultimately drive their organizations toward sustained success. Embracing these key ERP acronyms is not merely a trend; it is a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to navigate the complexities of today’s marketplace effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 10X ERP?
10X ERP is a cloud-based software designed specifically for growing distributors, focusing on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) to help manage operations efficiently from any location.
What are the key features of 10X ERP?
Key features of 10X ERP include a modern, user-friendly interface accessible via any web browser and real-time data processing capabilities, which provide immediate access to critical information for informed decision-making.
How is the cloud ERP market currently performing?
The global cloud ERP market was valued at USD 34.83 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 110.26 billion by 2030, indicating robust growth driven by increased adoption of cloud solutions.
What are the benefits of using cloud ERP solutions?
Cloud ERP solutions improve information accuracy and operational efficiency, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to market changes and customer demands, which is essential for modern distribution management.
What does the ERP acronym stand for?
The ERP acronym stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, which refers to integrated management of core business processes through sophisticated software and technology.
How prevalent is ERP software among wholesalers and distributors?
92% of wholesalers and distributors leverage ERP software, highlighting its importance in the industry.
What improvements do companies experience after implementing ERP solutions?
95% of companies report process improvements after implementing ERP solutions, with 89% citing efficiency enhancements as a primary benefit.
What are some advantages of using an ERP system?
Advantages of ERP systems include reduced process time, enhanced collaboration, and a centralized information framework, leading to optimized inventory levels for 91% of companies.
What challenges do organizations face with ERP project implementations?
Only 11% of ERP projects go live as scheduled, indicating challenges organizations encounter during implementation.
What is CRM and how does it integrate with ERP?
Client Relationship Management (CRM) platforms manage interactions with clients and, when integrated with ERP systems, enhance data accuracy and improve client retention rates.
What are the benefits of integrating CRM with ERP solutions?
Companies that integrate CRM with ERP solutions report a 27% increase in client retention, a 41% increase in sales revenue, and improvements in sales productivity.
How significant is the CRM market projected to be in the future?
The CRM market is projected to reach $145.61 billion by 2029, highlighting the growing importance of CRM solutions in business operations.
