Loss prevention refers to the steps businesses take to reduce profit loss through theft, cybercrime, fraud, and human errors. Loss prevention is not only an important part of remaining profitable but also improves customer satisfaction and employee health and safety.
What Is Loss Prevention?
Loss prevention has several definitions. Retail loss prevention, for example, refers to shrinkage due to stock damage and shoplifting. In occupational health circles, loss prevention refers to the procedures manufacturers take to prevent accidents or the loss of life. And in IT-heavy organizations, loss prevention often refers exclusively to data loss prevention, e.g., through data leaks or poor cyber hygiene.
For the purposes of this article, we’ll define loss prevention as any activity designed to minimize preventable losses through purposeful or accidental actions carried out by customers, employees, or any other individual that interacts with the business. We’ll also look at some of the key security and prevention measures your business should consider as part of your overall loss prevention strategy.
The Common Causes of Losses
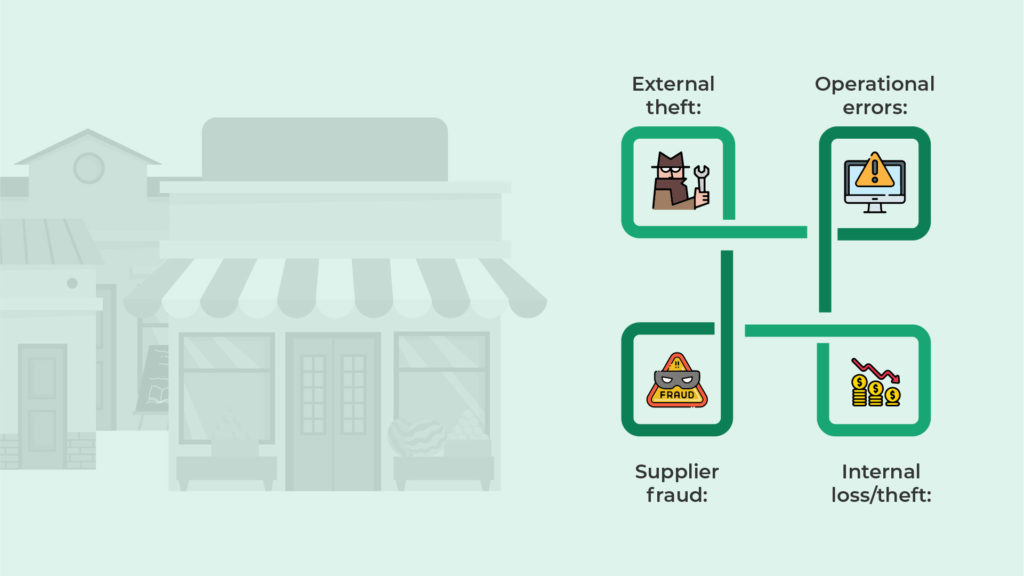
Losses are part and parcel of doing business, but it’s important to keep these losses to a minimum by improving your business processes, including stock handling and data access. Some of the common causes of loss within a business include:
- Operational errors: If employees aren’t trained properly, or if there aren’t good protocols in place, human error creeps in easily. Administrative errors are also widespread in business environments that rely heavily on manual data entry to operate.
- Internal loss/theft: Internal loss refers to any losses caused by employees or any other stakeholders that interact with the business, including package pilferage, passing discounts to family and friends, internal theft, wastage, vandalism, or fraud.
- External theft: External theft refers to profit loss that occurs as a result of the actions of external parties, e.g., shoplifting, vandalism, fraudulent returns, and so forth.
- Supplier fraud: Supplier fraud is far less common than internal theft or operational errors, but there is always the possibility that your business may interact with an unscrupulous supplier that fails to provide the correct amount of goods or facilitates fraud in other ways.
Why Your Business Needs a Loss Prevention Strategy
Loss prevention is a significant issue for retail stores and manufacturing organizations, but profit loss affects nearly every industry. Loss prevention strategies are important for several reasons – first and foremost, to protect your business and its bottom line.
Preventing inventory shrinkage, for example, is key to ensuring that the correct amount of inventory available for customers to purchase. Implementing proper training and procedures in your warehouse can reduce deterioration and damage, which leads to wastage. Instilling a culture of responsibility and safety will also increase employee morale, reduce employee theft, help employees feel invested in their job and the role they have to play to make the company successful.
Admin errors may seem minor, but history has shown us that simple human error can cost a company millions. In more recent years, high-profile data breaches have crippled many businesses. Data loss prevention strategies save money and considerable reputational damage to the business if implemented correctly.
The latter is particularly important for companies that use enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions to store all of their integral data and help run their business. Data loss prevention is not only important, but it’s also essential. The good news is that your ERP system can provide the insight you need to discover and reduce losses within your business, as shown in the section below.
Loss Prevention Strategies Every Business Should Follow

Loss prevention is an ongoing process that should regularly evolve to current needs. Here are just a few of the effective strategies you should consider implementing as part of your loss prevention strategy:
Point-of-Sale (POS) Upgrades
Many modern POS systems have additional security and prevention measures implemented and designed to uncover losses, including a management interface that requires employees to log in and out.
Loss Prevention Training
Loss prevention should form part of your culture and new-hire onboarding process. Staff should know how to minimize damage to stock, prevent shoplifting or stock theft, and how to handle returns effectively.
Track Loss Trends
Start monitoring loss trends in your company. Losses can easily go unnoticed, so tracking losses over time may reveal where and when losses are occurring (and who may be responsible for them). For example, you may notice that your till keeps coming up short when certain employees work or that you consistently see an increase in damage during the rainy season, indicating that you may need to weatherproof your warehouse. Accounts that are flagged for regular losses should be audited.
Evaluate Your Data Security
ERP systems are extensive, but many were built before modern security became standard. This means that vulnerabilities can be overlooked in most legacy systems currently on the market. Breaches can affect a single component and spread to the rest of the system, including the systems that house your financial data. Older ERP solutions are also more vulnerable to external threats, and they may not be compatible with upgrades, so consider migrating to a new system if you can’t implement the necessary patches.
Permission Management
Make sure that no one has unregulated access to important information and that discounts or freebies can’t be initiated without proper authorization. Always maintain a clear Segregation of Duties (SoD) that establishes levels of accessibility in your system. If data integrity issues pop up, ensure that you have adequate visibility into your systems to address them. Regular, automated reporting can also inform managers of instances of authorized data access and highlight flaws in your loss prevention efforts.
Conclusion
Loss may be an inevitable part of doing business, but many losses are preventable. By implementing a loss prevention strategy, your business will reduce stock and retail shrinkage due to employee fraud, human error, damage, or any other actions that cost your business money.
Automation, streamlining, and greater efficiencies will not only curb losses that affect your hard-earned profits but can go a long way towards keeping your customers and employees happy and productive. If you’re considering implementing or upgrading your ERP as part of a loss prevention strategy, talk to us at 10X ERP. We’re in the business of making your business more profitable.
