Overview
This article delves into the meaning and significance of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) within the realm of supply chain management. WMS plays a pivotal role in optimizing warehouse operations and logistics, and its importance cannot be overstated. By enhancing inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and operational efficiency, WMS directly contributes to reduced costs and improved customer satisfaction. The evidence lies in numerous successful implementations and promising market growth projections that underscore its value.
Consider how WMS transforms the landscape of logistics: it streamlines processes, allowing for real-time visibility and control over inventory. This not only accelerates order fulfillment but also minimizes errors, leading to a more efficient operation overall. As companies increasingly recognize these advantages, the demand for WMS solutions continues to rise, reflecting a broader trend towards automation and efficiency in supply chain practices.
In conclusion, the integration of WMS is not just a technological upgrade; it is a strategic move that can redefine operational success. For Operations Managers seeking to enhance their warehouse capabilities, investing in a robust WMS could be the key to unlocking significant improvements in both performance and customer satisfaction.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) is essential for businesses aiming to enhance supply chain efficiency. In an era where organizations grapple with increasing customer demands and the complexities of logistics, WMS emerges as a vital tool. It streamlines operations, optimizes inventory management, and improves order fulfillment.
Yet, as technology evolves, so too do the challenges and considerations surrounding WMS implementation. What key features define a successful WMS? How can companies leverage these systems to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market? These questions are critical for navigating today’s dynamic landscape.
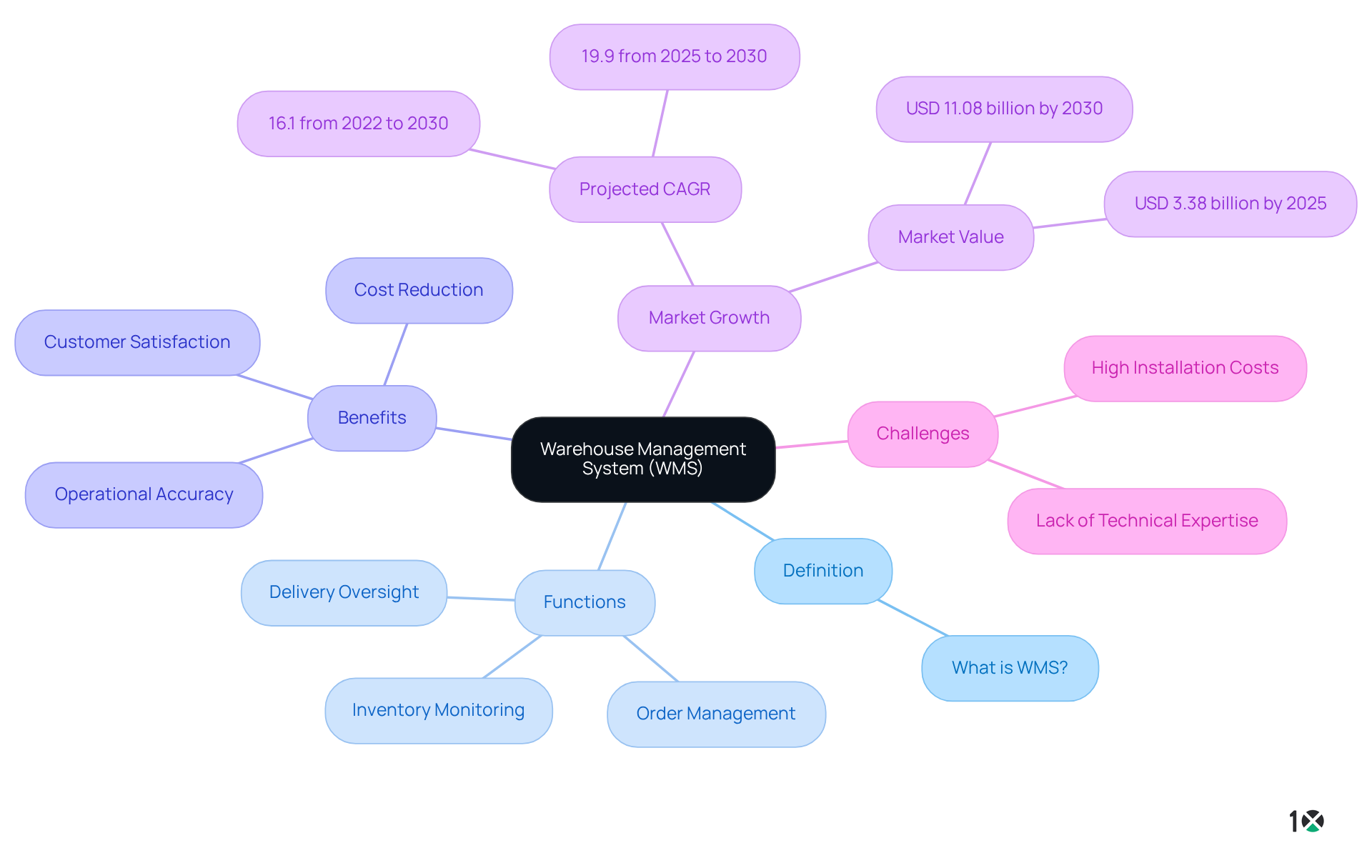
Define Warehouse Management System (WMS)
The wms meaning refers to a Warehouse Management System (WMS), which serves as a sophisticated software solution tailored to streamline and optimize warehouse operations. This powerful tool enables organizations to efficiently monitor inventory levels, manage orders, and oversee deliveries, ensuring that goods are stored and retrieved with optimal effectiveness. By controlling daily warehouse activities—from receiving and storing products to picking, packing, and shipping—WMS software significantly enhances operational accuracy and efficiency.
With real-time awareness of stock and processes, companies can dramatically improve their , leading to reduced operational expenses and increased customer satisfaction. In fact, organizations utilizing WMS solutions have reported logistics expenses reduced by as much as 15%, while those with streamlined processes have experienced cash-to-cash cycles that are three times quicker.
The global WMS market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 16.1% from 2022 to 2030, reaching USD 11.08 billion. This growth is driven by evolving logistics models adopted by product manufacturers and a rapidly increasing customer demand. However, challenges such as high installation costs and a lack of technical expertise may impede market growth. This underscores the critical role of WMS, or wms meaning, in modern logistics, making it an essential consideration for operations managers seeking to enhance their efficiency and effectiveness.
Contextualize WMS in Supply Chain Management
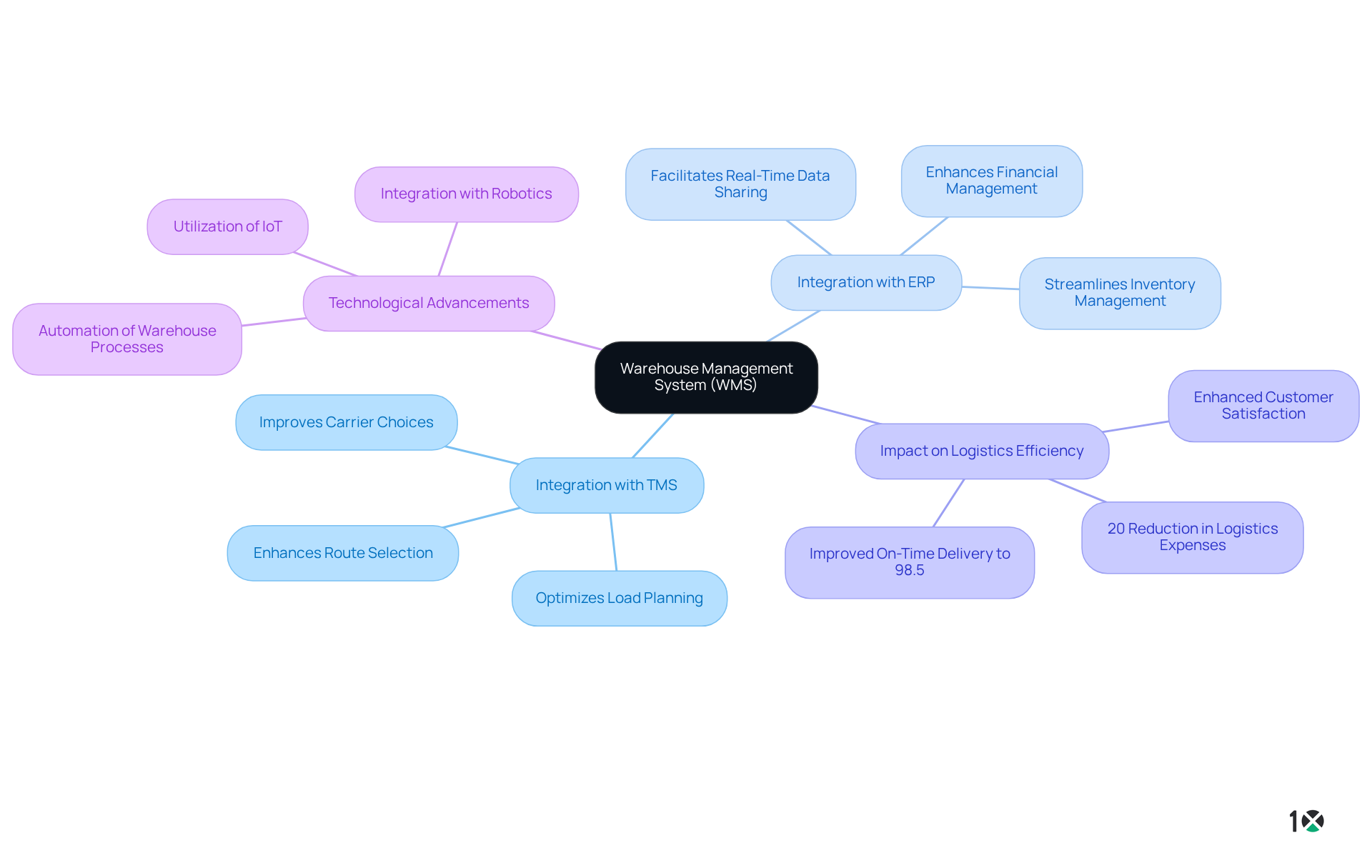
In the realm of logistics management, the WMS meaning highlights how a [Warehouse Management System](https://hqsoftwarelab.com/blog/custom-wms-integrations) serves as a critical component that bridges inventory management and order fulfillment. It is instrumental in guaranteeing product availability, thereby minimizing lead times and enhancing customer satisfaction. By automating various warehouse processes, WMS significantly boosts the overall effectiveness of the logistics network, empowering businesses to swiftly respond to market demands and maintain a competitive advantage.
For instance, ODW Logistics achieved a remarkable 20% reduction in logistics expenses and improved on-time delivery to 98.5% through effective WMS integration. The synergy of WMS with other systems, such as (TMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, amplifies its capability in managing the flow of goods from suppliers to customers. Notable examples, like the integration of CORAX WMS with BlueRock TMS, demonstrate how WMS can substantially elevate operational performance.
As organizations increasingly recognize the significance of integrated systems, the demand for WMS solutions that seamlessly connect with ERP and TMS continues to grow, highlighting the WMS meaning in current trends of logistics optimization. Moreover, advancements in technologies such as robotics and IoT are enhancing operational performance through WMS integration, making it imperative for Operations Managers to incorporate these innovations into their strategies.
Trace the Evolution of WMS
The evolution of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) highlights the WMS meaning rooted in the early days of manual inventory tracking, where paper logs and physical counts were commonplace. As technology advanced, the introduction of computerized systems in the 1970s marked a pivotal turning point in the industry. The first generation of WMS primarily focused on basic inventory control and order processing, laying the groundwork for future developments.
Over the years, advancements such as barcode scanning and RFID technology have enabled more sophisticated functionalities. These innovations have facilitated real-time inventory tracking and automated picking processes, significantly enhancing operational efficiency. Today, contemporary WMS solutions leverage , artificial intelligence, and machine learning to optimize warehouse operations. This evolution not only enhances decision-making but also improves overall supply chain performance, which emphasizes the WMS meaning as an indispensable tool for modern businesses.
In this rapidly changing landscape, it is crucial for Operations Managers to stay informed about these advancements. Embracing modern WMS solutions can lead to substantial improvements in productivity and accuracy, ultimately driving success in the competitive market.
![]()
Identify Key Features and Functionalities of WMS
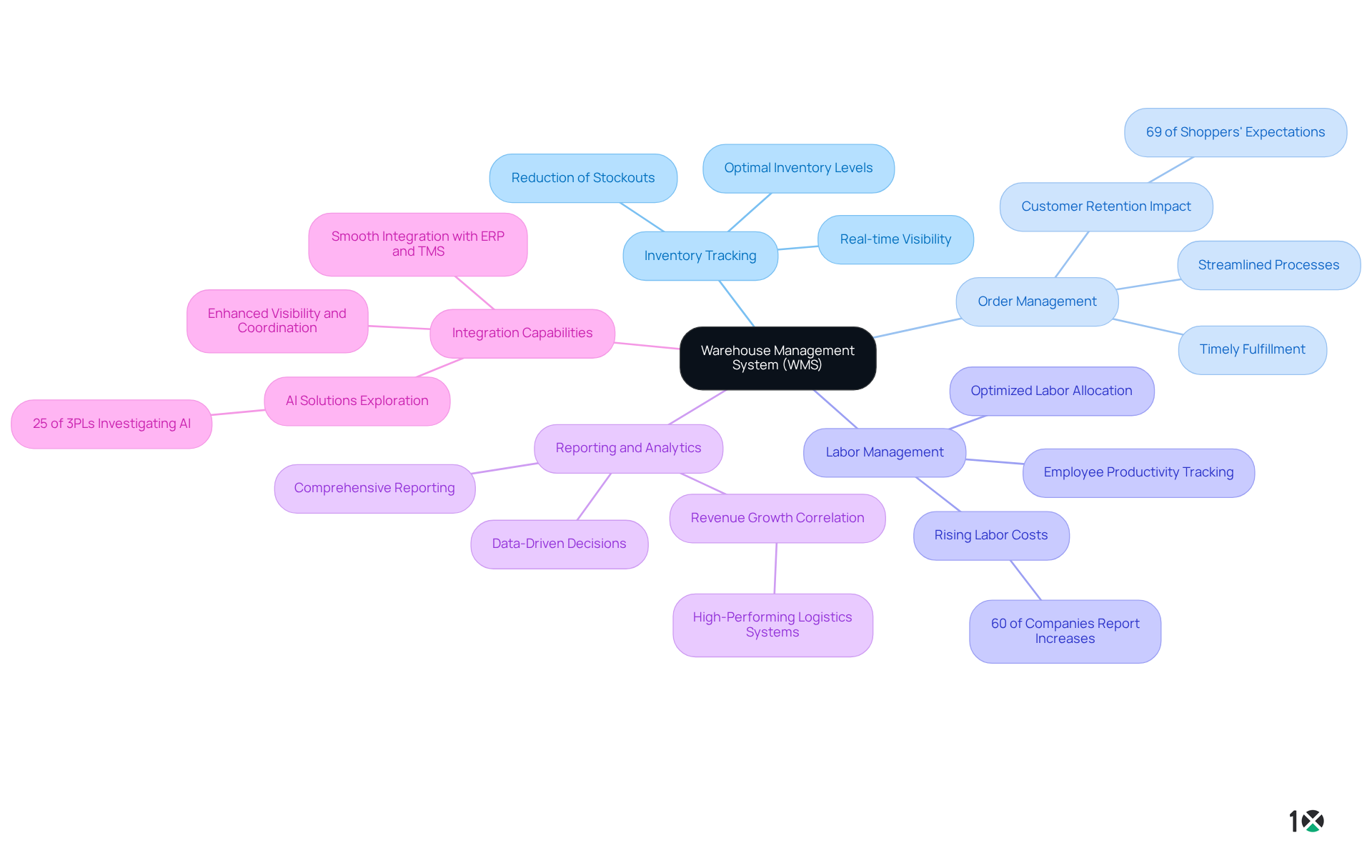
Key features of a Warehouse Management System (WMS) are essential for optimizing logistics operations:
- Inventory Tracking: This feature provides real-time visibility into stock levels, locations, and movements within the warehouse. Such transparency enables organizations to maintain optimal inventory levels and significantly reduce stockouts.
- Order Management: WMS streamlines processes for receiving, picking, packing, and shipping orders, ensuring timely fulfillment. This efficiency is vital, as 69% of shoppers are unlikely to return to a retailer if their order does not arrive within two days of the promised delivery date.
- Labor Management: The system offers tools for tracking employee productivity and optimizing labor allocation based on demand. This capability is increasingly important, especially since 60% of companies in the logistics sector report rising labor costs, highlighting the necessity for organizations to adapt their labor strategies to maintain efficiency amidst increasing expenses.
- Reporting and Analytics: With comprehensive reporting capabilities, WMS provides insights into warehouse performance, empowering organizations to make data-driven decisions. Notably, organizations with high-performing logistics systems achieve revenue growth exceeding the industry average, underscoring the significance of efficient analytics.
- Integration Capabilities: WMS guarantees smooth integration with additional systems, such as ERP and TMS, which enhances overall visibility and coordination of resources. This integration is critical, as 25% of third-party logistics providers (3PLs) are actively investigating AI solutions to further improve operational performance.
Together, these functionalities enable organizations to , lower operational expenses, and increase customer satisfaction. This highlights the WMS meaning as a crucial element of contemporary logistics management. As Wael Safwat aptly stated, “It’s not the organizations that are competing. It’s the supply chains that are competing,” emphasizing the critical role of WMS meaning in maintaining a competitive edge.
Conclusion
The significance of a Warehouse Management System (WMS) in supply chain management is paramount. This essential software solution not only enhances the efficiency of warehouse operations but also plays a pivotal role in optimizing logistics processes. By enabling real-time inventory tracking, streamlined order management, and seamless integration with other systems, WMS empowers organizations to effectively meet customer demands while minimizing operational costs.
Throughout this article, we have explored the critical functions of WMS, including its ability to:
- Automate warehouse processes
- Improve labor management
- Provide valuable insights through reporting and analytics
The evolution of WMS from manual tracking methods to advanced technologies like AI and cloud computing underscores its importance in modern logistics. Moreover, compelling case studies illustrate how businesses have achieved significant reductions in logistics expenses and improved service levels through effective WMS implementation.
In light of these insights, investing in a robust Warehouse Management System is not merely an operational choice; it is a strategic necessity for organizations aiming to thrive in today’s competitive landscape. As the demand for efficient supply chain solutions continues to grow, embracing WMS technology will be crucial for enhancing performance, driving customer satisfaction, and ultimately securing a competitive edge in the market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a sophisticated software solution designed to streamline and optimize warehouse operations, enabling organizations to monitor inventory levels, manage orders, and oversee deliveries effectively.
How does WMS improve warehouse operations?
WMS enhances warehouse operations by controlling daily activities such as receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping products, which leads to improved operational accuracy and efficiency.
What are the benefits of using a WMS?
Benefits of using a WMS include real-time awareness of stock and processes, reduced operational expenses, and increased customer satisfaction. Organizations have reported logistics expenses reduced by up to 15% and faster cash-to-cash cycles.
What is the projected growth of the WMS market?
The global WMS market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 16.1% from 2022 to 2030, reaching USD 11.08 billion.
What factors are driving the growth of the WMS market?
The growth of the WMS market is driven by evolving logistics models adopted by product manufacturers and a rapidly increasing customer demand.
What challenges might affect the growth of the WMS market?
Challenges such as high installation costs and a lack of technical expertise may impede the growth of the WMS market.