Overview
The role of an ERP analyst is pivotal in managing and optimizing ERP systems, aimed at enhancing organizational efficiency. This involves key responsibilities such as:
- System implementation
- Data analysis
- User support
Proficiency in both technical and soft skills is essential, as is a deep understanding of business processes. Such expertise enables ERP analysts to align ERP solutions effectively with organizational goals, driving successful deployments. Ultimately, the effectiveness of an ERP analyst can significantly influence an organization’s operational success.
Introduction
In today’s technology-driven landscape, the role of an ERP Analyst has become increasingly vital as organizations strive for operational efficiency and data accuracy. By effectively bridging the gap between technical teams and business stakeholders, ERP analysts not only optimize enterprise resource planning systems but also enhance overall organizational performance.
However, with the growing complexity of these systems and the rising stakes, evidenced by a significant failure rate in implementations, it is crucial to consider what skills and strategies are essential for ERP analysts to navigate this challenging environment effectively.
Define the ERP Analyst Role
An ERP analyst, or Enterprise Resource Planning Analyst, plays a crucial role in managing and optimizing an organization’s ERP solutions. The ERP analyst is responsible for analyzing business processes, implementing tailored ERP solutions, and ensuring that the software effectively meets the organization’s specific needs. By collaborating closely with various departments, ERP professionals streamline operations, enhance data integrity, and improve overall efficiency. Their distinctive combination of knowledge in information technology and business processes enables them to act as an essential connection between technical teams and business stakeholders, ensuring that the ERP solution aligns effortlessly with organizational objectives.
As companies increasingly depend on ERP systems to enhance efficiency and data precision, the need for proficient ERP analysts keeps rising. The job growth rate is expected to be 9% from 2018 to 2028. In 2025, the average salary for ERP professionals is anticipated to vary from $54,000 to $121,000, indicating the essential nature of their contributions to contemporary businesses. Additionally, it is important to note that 58.2% of ERP professionals are male and 41.8% are female, highlighting the demographic landscape within the profession.
Soft skills such as communication and adaptability are also essential for ERP professionals to succeed in their roles. ERP Analysts frequently utilize user manuals and FAQs to enhance their understanding of the ERP solutions they manage, ensuring they can effectively assist users and optimize functionality. Their role is further complemented by the of 10X ERP, which facilitate seamless integration and real-time data processing, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency.
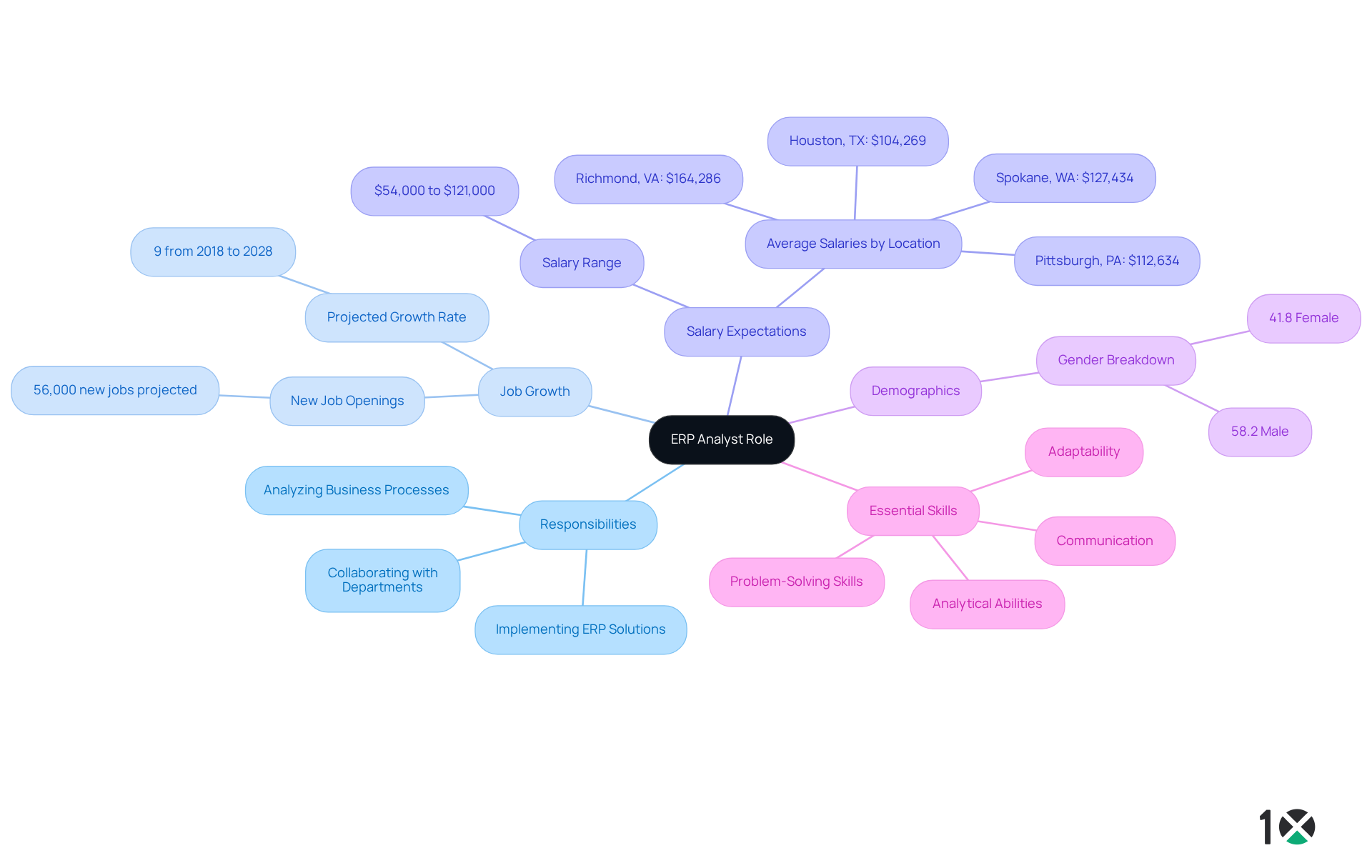
Trace the Evolution of ERP Analysts
The role of the ERP Analyst has undergone a significant transformation since the inception of ERP technologies in the 1960s, which primarily focused on Material Requirements Planning (MRP). As organizations recognized the necessity for integrated frameworks to enhance resource management, the responsibilities of ERP analysts expanded considerably. By the 1990s, with the rise of comprehensive ERP systems, ERP analysts began to focus on customizing and optimizing these solutions to meet the distinct needs of various organizations.
Today, ERP analysts are expected to integrate technical expertise with business acumen, as well as possess a profound understanding of emerging technologies such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence. This evolution underscores the dynamic nature of the role, as ERP professionals must consistently adapt to the shifting technological landscape and the growing complexity of business operations. Notably, 50% of ERP implementations fail on the first attempt, underscoring the challenges that ERP analysts encounter in securing successful deployments.
Furthermore, with the [cloud ERP market projected to reach $140 billion by 2030](https://netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/erp/erp-statistics.shtml), the increasing significance of [cloud solutions like 10X ERP](https://10xerp.com) becomes apparent. This platform delivers , optimized inventory management, and seamless integrations—key elements for improving data accuracy and user experience. As they navigate these complexities, an ERP analyst must leverage the user-centric features and transparent pricing of modern ERP solutions to maximize the effectiveness of ERP tools.
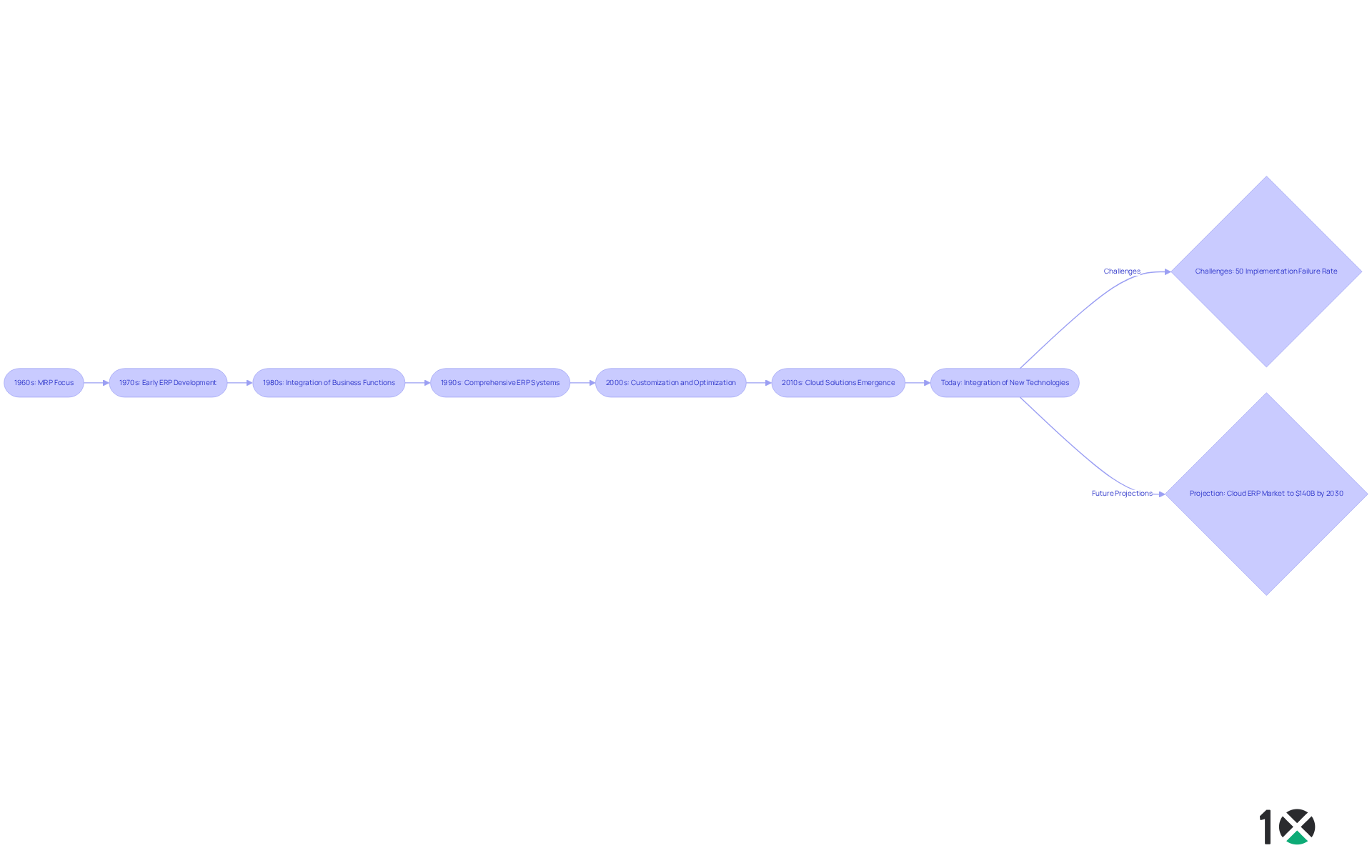
Outline Key Responsibilities of ERP Analysts
ERP Analysts play a pivotal role in maximizing the effectiveness of ERP systems through a variety of responsibilities:
- System Implementation: They oversee the deployment of ERP systems, ensuring that configurations align with specific business requirements. This meticulous supervision is essential; organizations investing in extensive education during implementation report adoption rates up to 70% quicker than those with inadequate preparation. Moreover, thorough instruction combined with continuous support minimizes system-related issues by as much as 60%, emphasizing the vital importance of education in implementation. With 10X ERP’s commitment to user-driven development and its API-first approach, the onboarding process is streamlined, allowing for real-time status updates and , ensuring that operations managers can focus on delivering value to their customers.
- The ERP analyst customizes and optimizes the software to enhance functionality and improve user experience. Customization can result in considerable operational enhancements, with companies prioritizing personalized development experiencing 50% greater user satisfaction compared to those utilizing standard programs. 10X ERP’s powerful cross-referencing and customizable attributes in inventory management, combined with its seamless integration capabilities, further enhance this experience, ensuring that the software meets the unique needs of each organization.
- Data Analysis: The ERP analyst analyzes data to identify trends, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement within business processes. Effective data analysis enables organizations to make informed decisions, with 95% of companies reporting improved business processes after ERP deployment. Furthermore, companies incorporating problem-solving exercises in their ERP programs see a 45% enhancement in cross-departmental teamwork, illustrating the effect of effective instruction on data analysis and collaboration.
- Offering education to end-users and continuous support is crucial for ensuring effective use of the ERP analyst’s system. Organizations investing in high-level training achieve an ERP adoption success rate of 85%, while low-level training programs achieve only a 30% success rate, highlighting the necessity of comprehensive training to equip employees with the necessary skills. 10X ERP enhances user experience with in-app video guides created by the developers, allowing users to find answers quickly without leaving the application.
- Collaboration is essential, as ERP Analysts work with cross-functional teams to gather requirements, troubleshoot issues, and implement solutions that align with business objectives. This cooperative method not only improves functionality but also promotes a culture of accountability and involvement among employees. Aligning ERP training with change management strategies helps employees understand the reasons behind changes, further enhancing collaboration. With 10X ERP’s personalized support, users can always reach out for assistance, ensuring that their needs are met promptly.
These responsibilities highlight the vital role that ERP analysts fulfill in guaranteeing that ERP solutions provide significant value to organizations, ultimately enhancing efficiency and productivity.
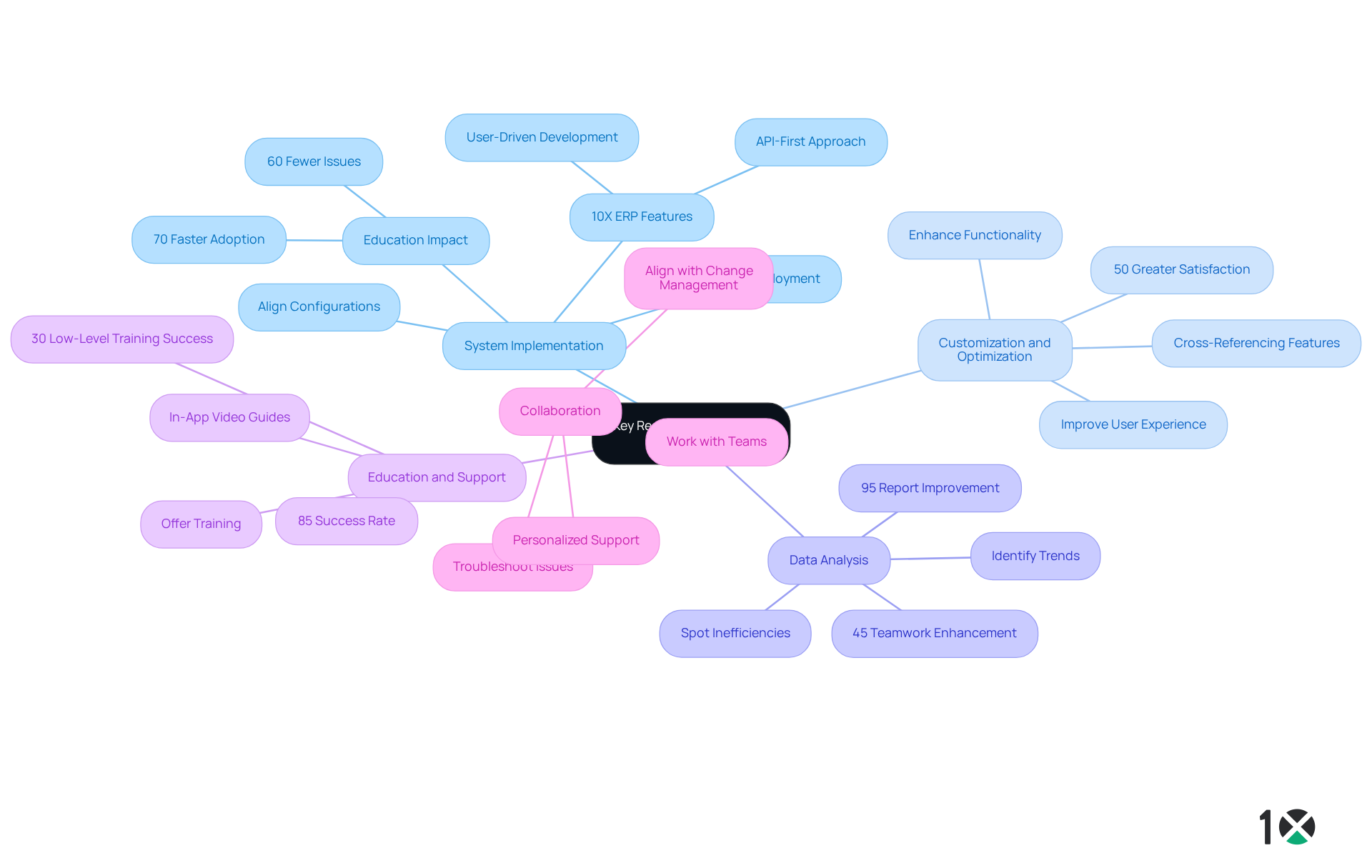
Identify Essential Skills and Qualifications
To excel as an ERP Analyst, individuals must possess a blend of technical and soft skills that are essential for navigating the complexities of the and contributing significantly to their organizations’ success.
- Technical Proficiency: A robust understanding of ERP systems such as SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft Dynamics is crucial. This knowledge enables analysts to effectively navigate and leverage these platforms, ensuring optimal performance in their tasks.
- Analytical Skills: The ability to analyze complex data sets and extract actionable insights is vital. Experts must be skilled at interpreting data to guide strategic decisions, ultimately driving organizational success.
- Problem-Solving: A strong aptitude for identifying issues and developing effective solutions is essential. This skill ensures that analysts can address challenges proactively, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Communication Skills: Effective verbal and written communication skills are necessary for collaborating with stakeholders and conveying technical information clearly. This facilitates smoother interactions across departments, enhancing overall productivity.
- Project Management: Experience in managing projects, including planning, execution, and monitoring, is important. Analysts often oversee various initiatives, making project management skills indispensable for achieving project goals.
- Educational Background: Generally, a bachelor’s degree in information technology, business administration, or a related area is necessary, along with pertinent certifications in ERP platforms. Statistics indicate that 85% of organizations report successful ERP projects when hiring professionals with the right educational qualifications.
- User Acceptance and Integration: Recognizing the significance of user acceptance is essential, as the success of ERP solutions depends on how effectively they are embraced by end users. Additionally, ERP professionals must ensure proper integration of ERP systems with other enterprise software applications to maximize their effectiveness.
These skills and qualifications are not merely desirable; they are fundamental to the role of an ERP Analyst, as they underpin the ability of an ERP Analyst to drive success within their organizations.
Conclusion
The role of an ERP analyst is integral to the success of modern organizations, serving as a critical bridge between technology and business processes. By understanding and optimizing ERP systems, these professionals ensure that businesses operate efficiently and effectively, ultimately driving growth and innovation.
Key points highlighted throughout the article include:
- The evolution of the ERP analyst role
- The essential responsibilities they undertake
- The critical skills required to excel in this position
From system implementation and data analysis to collaboration and user education, ERP analysts play a multifaceted role that directly impacts organizational performance. The increasing demand for these professionals, coupled with their significant contributions to ERP success, underscores the importance of their expertise in today’s business landscape.
As organizations navigate increasingly complex technological environments, the value of proficient ERP analysts becomes unmistakably clear. Investing in the development of these professionals not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Embracing the evolving nature of the ERP analyst role is crucial for businesses aiming to remain competitive and responsive to market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of an ERP Analyst?
An ERP Analyst, or Enterprise Resource Planning Analyst, is responsible for managing and optimizing an organization’s ERP solutions by analyzing business processes, implementing tailored ERP solutions, and ensuring the software meets the organization’s specific needs.
How do ERP Analysts contribute to an organization?
ERP Analysts streamline operations, enhance data integrity, and improve overall efficiency by collaborating closely with various departments. They act as a connection between technical teams and business stakeholders to ensure the ERP solution aligns with organizational objectives.
What is the job growth rate for ERP Analysts?
The job growth rate for ERP Analysts is expected to be 9% from 2018 to 2028.
What is the anticipated salary range for ERP professionals in 2025?
The average salary for ERP professionals in 2025 is anticipated to vary from $54,000 to $121,000.
What is the gender demographic of ERP professionals?
The demographic landscape within the ERP profession shows that 58.2% of ERP professionals are male and 41.8% are female.
What soft skills are important for ERP Analysts?
Important soft skills for ERP Analysts include communication and adaptability, which are essential for succeeding in their roles.
How do ERP Analysts enhance their understanding of ERP solutions?
ERP Analysts frequently utilize user manuals and FAQs to enhance their understanding of the ERP solutions they manage, enabling them to assist users effectively and optimize functionality.
What features of 10X ERP support ERP Analysts in their roles?
The user-centric features of 10X ERP facilitate seamless integration and real-time data processing, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency for ERP Analysts.
