Overview
The fundamental distinctions between ERP and CRM systems are rooted in their core functions and target areas. ERP primarily concentrates on internal business processes, while CRM is dedicated to customer relationship management. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective operations management.
ERP systems significantly enhance operational efficiency through the integrated management of finance, supply chain, and human resources. In contrast, CRM systems are specifically designed to improve client interactions and streamline sales processes. This knowledge empowers operations managers to leverage the appropriate system, ultimately driving better business outcomes.
Introduction
The landscape of business operations is evolving rapidly, with organizations increasingly relying on technology to streamline processes and enhance customer relationships. For operations managers seeking to optimize efficiency and foster growth, understanding the distinct yet complementary roles of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems is essential. Yet, many face the challenge of navigating the complexities of these systems.
How can they effectively integrate ERP and CRM to maximize their benefits? This article delves into the key differences between ERP and CRM, exploring their functionalities, advantages, and the critical importance of their integration in driving business success.
Define ERP and CRM: Core Concepts and Functions
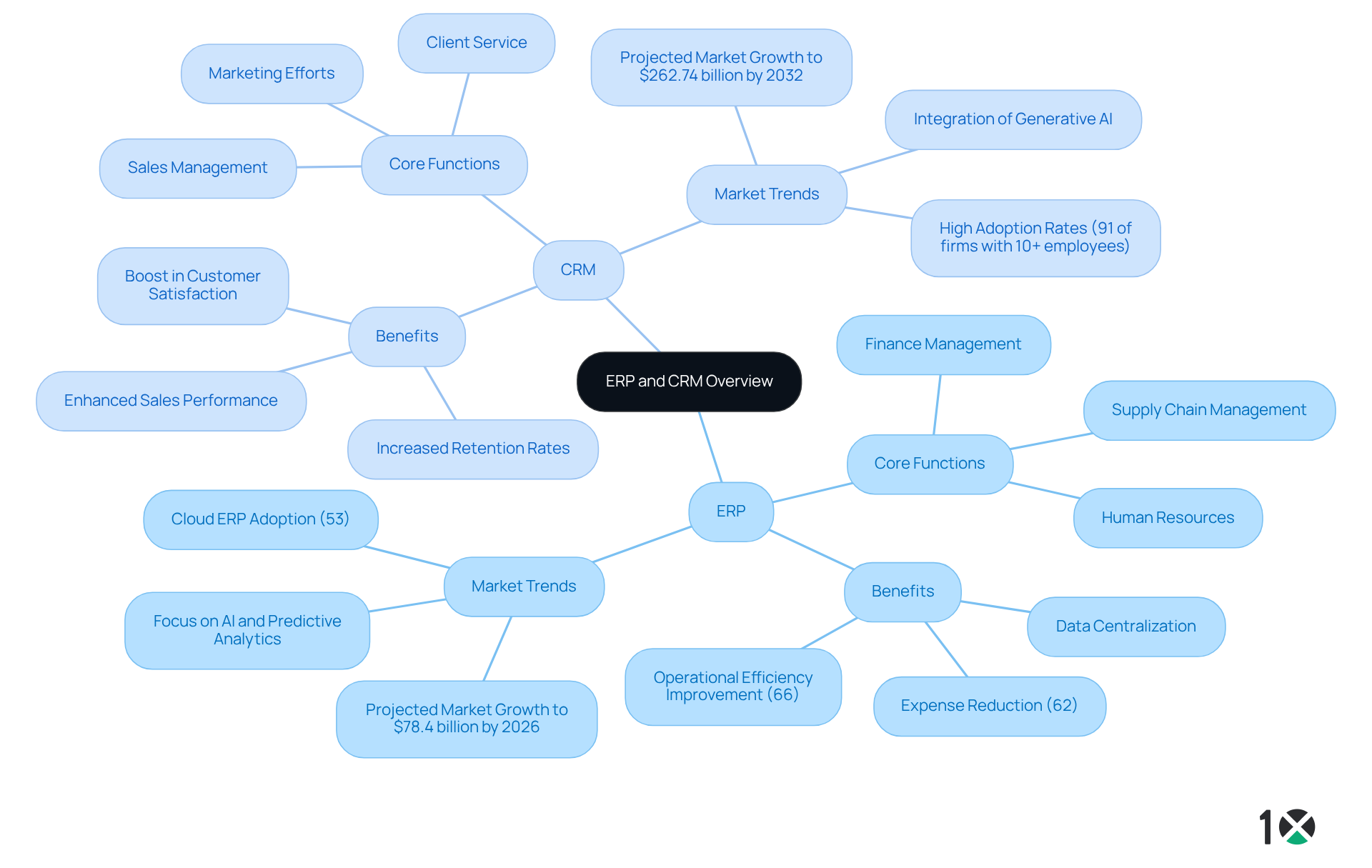
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) applications are comprehensive software solutions that integrate and manage core business processes across various departments—including finance, supply chain, and human resources. By centralizing data management, ERP solutions significantly enhance operational efficiency and empower informed decision-making. Organizations implementing ERP solutions frequently report a 66% improvement in operational efficiency and a 62% reduction in expenses, particularly in procurement and inventory management.
Conversely, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms are tailored to manage a company’s interactions with both existing and prospective clients. CRMs streamline sales management, client service, and marketing efforts, ultimately aiming to boost satisfaction and retention. Notably, 91% of firms with ten or more employees utilize a CRM solution, underscoring its critical role in fostering client relationships.
While ERP solutions focus on internal processes, CRMs are outward-facing, emphasizing . This distinction is crucial for operations managers, as understanding the complementary functions of ERP and CRM can lead to more effective integration strategies. As organizations increasingly recognize the importance of both frameworks, the global CRM market is projected to reach $262.74 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 12.6%. Similarly, the ERP market is also expected to experience substantial growth, reflecting the evolving landscape of business operations.
Compare Features: Key Functionalities of ERP vs. CRM
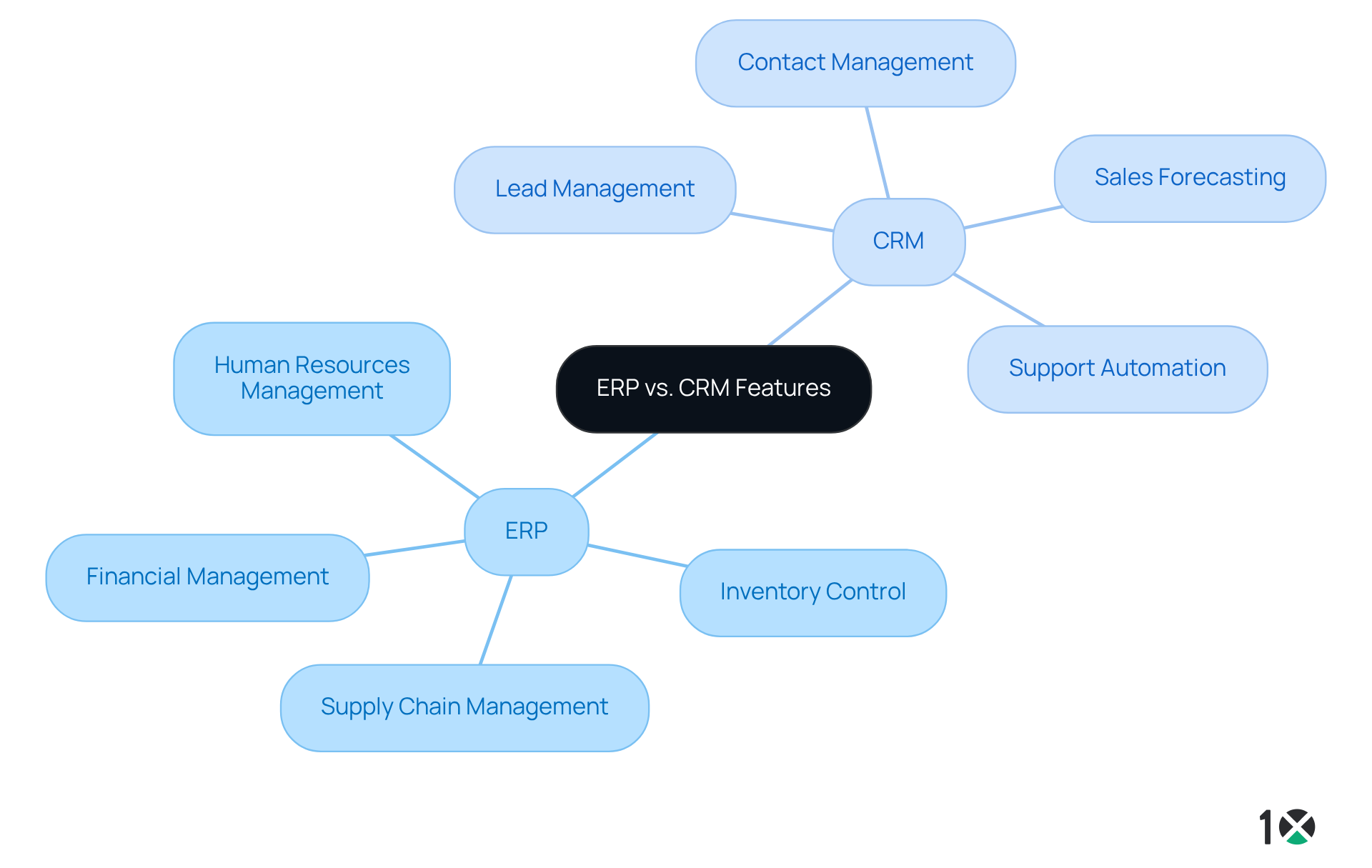
ERP solutions encompass a diverse range of functionalities, including:
- Financial management
- Inventory control
- Supply chain management
- Human resources management
These features empower organizations to automate and optimize internal processes, ensuring data accuracy and enhancing operational efficiency. Notably, 91% of organizations report improved inventory levels following ERP implementation, underscoring the tangible advantages these solutions provide. Conversely, CRM platforms focus on:
- Lead management
- Contact management
- Sales forecasting
- Support automation
Designed specifically to enhance client interactions and streamline sales processes, these tools highlight the distinct purposes of ERP and CRM systems. While some overlap exists in areas such as sales and customer information management, the primary features of ERP and CRM platforms address . Importantly, 78% of organizations have observed increased productivity due to ERP solutions, emphasizing their critical role in achieving operational success.
Evaluate Benefits: Advantages of ERP and CRM Systems
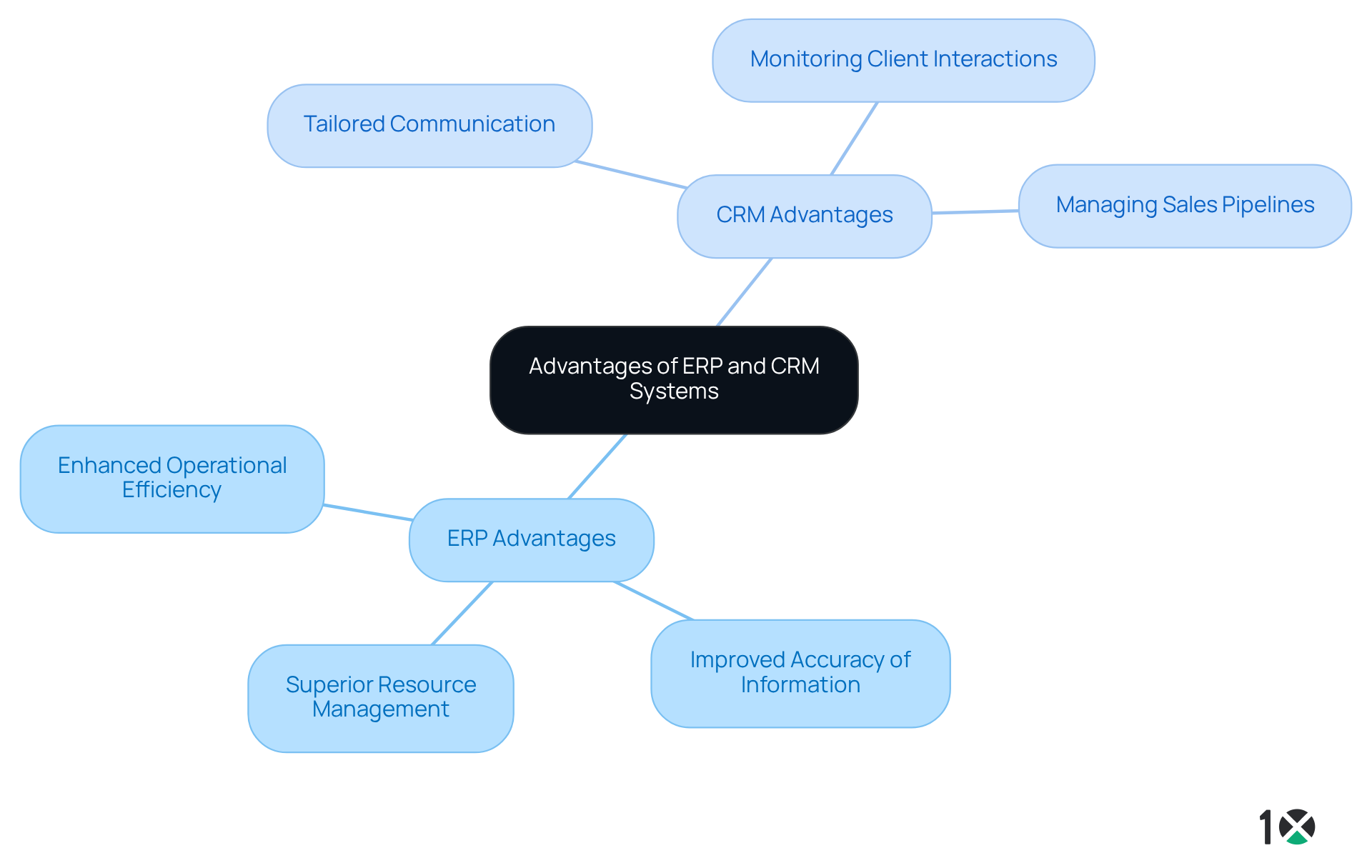
The primary advantages of ERP systems, such as 10X ERP, include:
- Enhanced operational efficiency through automation
- Improved accuracy of information
- Superior resource management
By integrating various business functions into a single platform, 10X ERP effectively minimizes information silos and facilitates real-time reporting, which is essential for informed decision-making. For example, its cloud-based architecture allows real-time access to data across multiple departments and locations, a critical component for effective management. Moreover, the software boasts best-in-class inventory management and seamless integrations, ensuring that distributors operate efficiently.
Conversely, CRM platforms significantly enhance client satisfaction by providing tools for:
- Tailored communication
- Monitoring client interactions
- Managing sales pipelines
Strong client relationships foster greater loyalty and retention rates, with studies showing that effective CRM implementation can lead to a 30% increase in client retention. As Chris Mellides notes, “CRM platforms provide significant benefits by centralizing customer information, improving relationships, and fostering business growth.” Ultimately, both frameworks, such as ERP and CRM, , albeit through different pathways. ERP solutions like 10X ERP streamline processes such as order management and inventory control, while CRM systems focus on nurturing customer relationships.
Explore Integration: Connecting ERP and CRM for Enhanced Performance
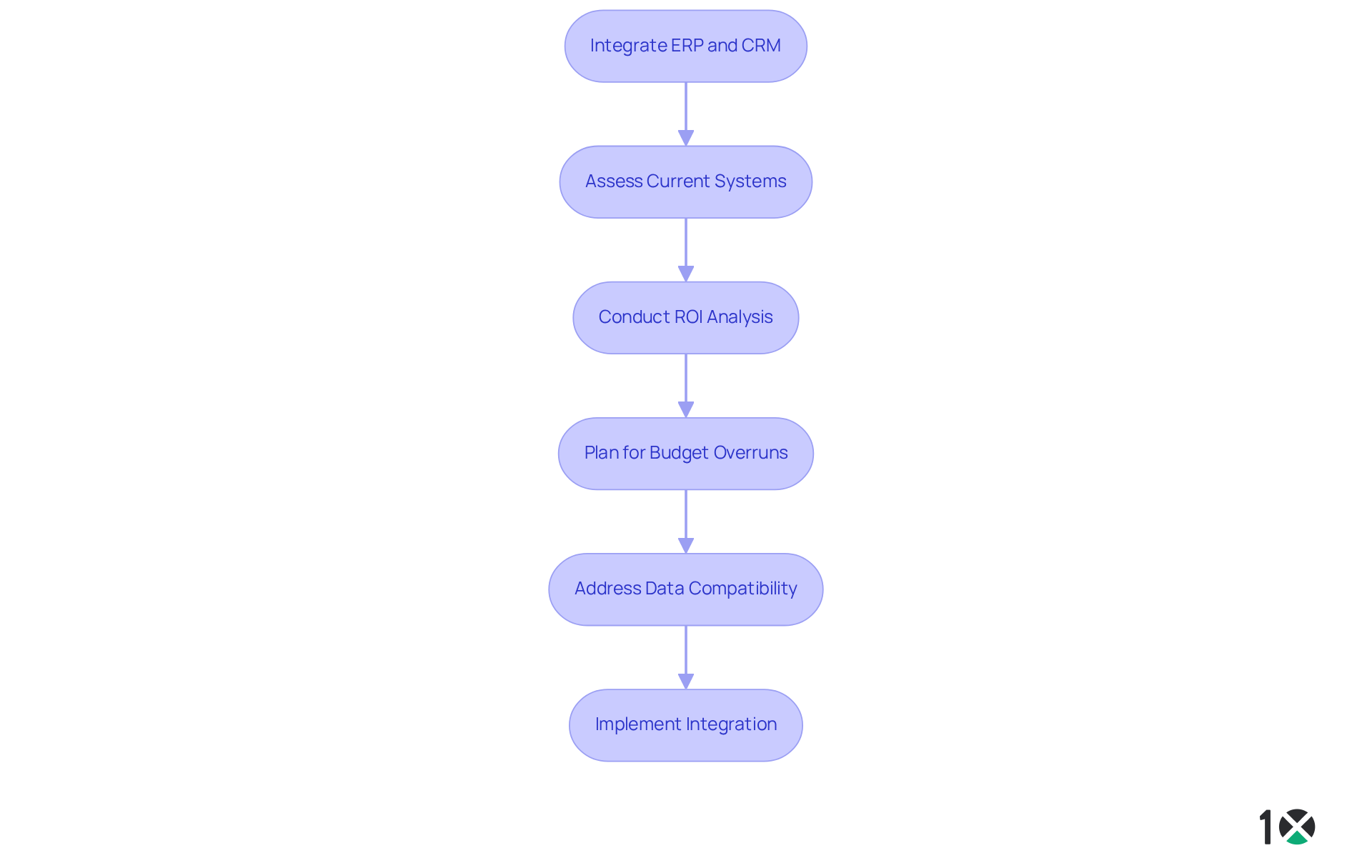
Integrating ERP and CRM solutions can significantly enhance business performance by aligning customer-facing and back-office functions. This integration enables , decreases manual input, and minimizes mistakes. For instance, sales teams can access real-time inventory information from the 10X ERP platform, allowing them to provide precise details to customers and enhance satisfaction. Furthermore, integrated solutions improve forecasting precision by merging sales information from the ERP and CRM with inventory and financial insights, resulting in more informed decision-making.
Designed specifically for wholesale distributors, 10X ERP offers innovative cloud-based solutions that ensure robust features and exceptional support. Its API-first strategy facilitates seamless integrations, enabling businesses to leverage real-time information processing for enhanced operational efficiency. The support beacon within the 10X ERP instance allows users to chat with support, log issues, and access documentation, ensuring assistance is readily available. However, successful integration necessitates careful planning and execution to address challenges such as data compatibility and interoperability. Statistics reveal that 51% of companies experience disruptions when implementing new ERP systems, underscoring the importance of addressing these challenges proactively.
Best practices for integration include:
- Conducting thorough ROI analyses, as 83% of businesses that perform such assessments achieve their expected outcomes.
- Being aware that most ERP projects exceed initial budgets by three to four times, highlighting the financial implications of integration challenges.
By prioritizing these strategies, organizations can leverage the full potential of ERP and CRM connectivity, ultimately driving improved operational efficiency and enhancing business performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems is vital for operations managers aiming to optimize business processes. ERP focuses on internal resource management and efficiency, while CRM is dedicated to enhancing customer interactions and satisfaction. Recognizing how these two systems complement each other can drive more effective integration strategies, ultimately leading to improved organizational performance.
The core functionalities of both systems are highlighted, with ERP providing tools for financial management, inventory control, and human resources, while CRM excels in lead management and sales automation. Each framework offers unique advantages that contribute to overall productivity and profitability, with ERP enhancing operational efficiency and CRM fostering client relationships. The integration of these systems can further streamline processes, improve data accuracy, and enhance decision-making capabilities.
In an increasingly competitive landscape, the synergy between ERP and CRM is not just beneficial but essential. Organizations prioritizing the integration of these systems can unlock significant performance improvements, ensuring they remain agile and responsive to market demands. Embracing these technologies and their interconnectedness is a strategic move that can lead to sustained growth and success in business operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) refers to comprehensive software solutions that integrate and manage core business processes across various departments, including finance, supply chain, and human resources.
What are the benefits of implementing ERP solutions?
Organizations implementing ERP solutions often report a 66% improvement in operational efficiency and a 62% reduction in expenses, particularly in procurement and inventory management.
What is Customer Relationship Management (CRM)?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms are designed to manage a company’s interactions with existing and prospective clients, streamlining sales management, client service, and marketing efforts.
How prevalent are CRM solutions among businesses?
Notably, 91% of firms with ten or more employees utilize a CRM solution, highlighting its critical role in fostering client relationships.
What is the main difference between ERP and CRM systems?
ERP solutions focus on internal processes within an organization, while CRM systems are outward-facing, emphasizing customer engagement and relationship development.
Why is it important for operations managers to understand ERP and CRM?
Understanding the complementary functions of ERP and CRM can lead to more effective integration strategies, enhancing overall business operations.
What is the projected growth for the global CRM market?
The global CRM market is projected to reach $262.74 billion by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.6%.
Is the ERP market also expected to grow?
Yes, the ERP market is expected to experience substantial growth, reflecting the evolving landscape of business operations.
