Summary
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) refers to software used by organizations to centralize and manage various business processes, including inventory, customer, and vendor management, accounting, and more, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- ERP systems have evolved since the 1960s and can now be deployed via cloud, on-premise, or hybrid models, with modern systems offering flexibility, accessibility, and improved compliance efforts.
- Industries such as distribution, manufacturing, healthcare, hospitality, and construction rely on ERP for various functions like inventory management, workforce coordination, and financial control, making it essential for profitable scaling and business optimization.
Enterprise resource planning refers to software used by organizations to manage their day-to-day business processes and activities, including inventory, customer, and vendor management, procurement, supply chain management, accounting, and more. Also known as ERP, these systems deliver an integrated suite of business applications supporting numerous functions through automation of common processes and centralization of data.
Most businesses invest in enterprise resource planning software to improve business process efficiency, standardize workflows, and reduce IT costs.
What Is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
Enterprise resource planning refers to a centralized platform used by organizations to manage and integrate essential operations within their business. An ERP solution assists companies with resource planning by integrating the various processes and key business functions required to run their business to a single system.
The first traces of ERP applications are found in the 1960s with the emergence of Material Requirements Planning (MRP I) systems, automated systems used to control and link inventories to production schedules. When groups of processes (including customer order data and accounting software) required optimization and unification, these early systems evolved into MRP II and MRP III. Soon, cross-enterprise systems were developed, resembling the ERP solutions we see today in the market.
Early ERP systems were sold as off-the-shelf solutions for collaboration and data management. Soon, companies began selling multiple ERP modules that were customizable and able to integrate with other software solutions.
Today, enterprise resource planning systems have evolved to become even more multi-faceted, flexible, and responsive. They are easily accessed via social, mobile, and cloud platforms, improving visibility to assist companies with their compliance efforts and operational oversight.
Different ERP Systems
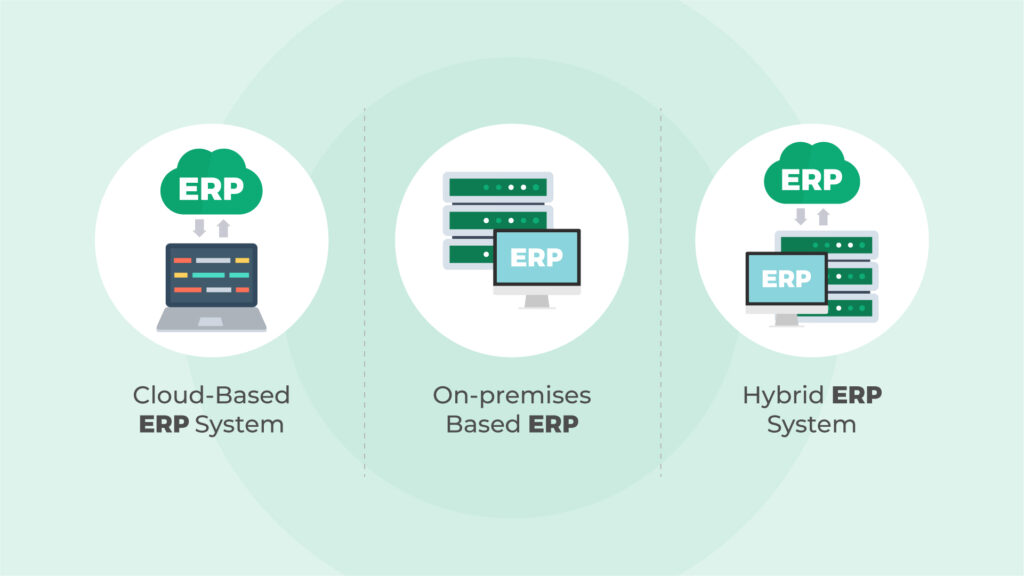
There are several ERP deployment models on the market, including cloud, on-premise, and hybrid models.
Cloud ERP system
Cloud ERP systems can be public or private. It refers to an ERP software system accessible over the Internet, providing advanced functionality for all of the core processes in the organization. Cloud ERP is usually delivered “as a service” (software-as-a-service or SaaS), whereby the technology is leased on a subscription basis from an ERP software provider. Cloud ERP vendors handle the server maintenance, upgrades, data storage, and security on behalf of the company.
On-premise ERP system
An on-premise enterprise resource planning system runs its applications on servers in the company’s own data centers, either in the organization’s premises or a private cloud. Software is leased or purchased, and the organization directly controls the servers’ storage acquisition and operation. Most ERP systems are cloud-based or hybrid, as on-premises ERP systems are generally more expensive to operate and maintain.
Hybrid ERP system
A hybrid ERP combines cloud and on-premise ERP systems. The organization operates critical business processes and applications with particular limitations under their control, in their own data center, or within a private cloud. Users can access applications or components from public clouds simultaneously, reducing the implementation time and cost.
How Does ERP Work?
ERP software is generally maintained by the company that created it, with clients renting services provided by the ERP platform provider. Businesses select the ERP modules or applications they would like to use, and the hosting company will implement the applications on the relevant server. Both parties work to integrate the various client processes and critical data found in disparate systems into the platform.
Once various departments tie into the system, data is collected in a centralized database on the server and made available to users with permission to access it. Reports can be generated by various parties to determine areas for improvement or optimization, or to track key business metrics.
Benefits of Enterprise Resource Planning
Companies invest in enterprising resource planning for a number of reasons, which vary depending on the company’s current system, its goals, and the industry it operates in.
ERP technology integrates and automates key business processes, which eliminates redundancies and improves productivity. Various departments can synchronize work and reduce duplication of efforts to achieve their goals more efficiently, access information needed for clients and business partners with ease, and reduce costs.
Instead of relying on manually tracking information, which is highly prone to errors and has significant lag in reporting, many businesses integrate an ERP for real-time data reporting. Accurate and comprehensive reports can be accessed from a single source of truth, which simplifies planning, budgeting, and forecasting and provides complete visibility across the entire organization.
As departments become more synergized through enterprise planning efforts, they’re empowered to collaborate and share knowledge. In addition to productivity gains, this empowerment provides a better understanding of the mission and vision of the organization.
Which Industries Use ERP software?
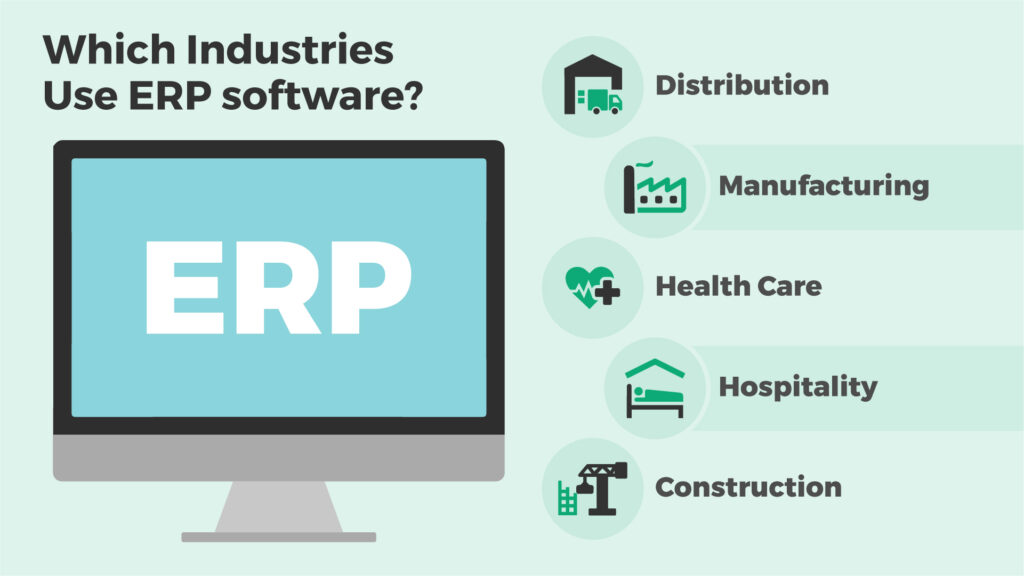
Virtually all industries can benefit from ERP software. Some of the key industries that depend heavily on ERP include:
Distribution
92% of distributors use ERP software to keep inventory low, minimize overheads and stock-outs, and to track orders. Distribution ERP software manages logistics, front – and back-office activities, and determines demand so that enough inventory is kept on hand and delivered on time.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies use ERP to manage facility operations, production, payroll, staff, and inventory. As the industry requires visibility, coordination, and close management across various disparate processes, an ERP is essential for manufacturers and distributors.
Health Care
Healthcare organizations must juggle patient care, payroll, workforce management, supplies, and compliance. The right ERP integration can help hospitals and medical companies optimize processes and improve operations.
Hospitality
The hospitality sector places great emphasis on workforce management, fast-moving maintenance operations, and customer relationship management. Automated workflows realized through ERP software can streamline and improve the way the hospitality sector operates.
Construction
The construction industry uses ERP to track various subcontractors, supplies, human resources, assets, and running costs. The analytical and project management capabilities that an ERP can provide can assist construction companies that require accuracy and close cost management and controls to remain profitable.
Conclusion
At its core, enterprise resource planning is designed to manage and integrate functions across an organization. Accounting & finance, inventory & warehousing, sales & purchasing, and HR & project management within a single unified system provides powerful insights that can’t be garnered when they are siloed.
ERP is used by businesses of all sizes and becoming a must for any company that wishes to scale profitably while optimizing its business processes. If you’d like to see what a modern ERP can do for your business, get in touch with us at 10X ERP.
