Whenever you have a new business idea, it’s important to do enough due diligence to determine whether or not it’s feasible. This could be a brand new, novel business idea or simply an expansion of your existing business – like modifying an existing product offering or expanding a specific department.
Your break-even point (BEP) reveals the moment your business idea becomes profitable. This informs what actions are needed before your, or your business’s, time and money is invested in this new venture. A good break-even analysis determines which price and cost adjustments you’ll need to make and whether or not it’s even worth pursuing to begin with.
What Is Break-Even Analysis?
Break-even analysis is a financial calculation used to determine at which point the company, product, business line, etc. revenues equal its costs. To calculate the break-even point, you’ll look at and adjust the number of units that need to be sold to break even along with the amount of sales dollars you need to bring in to reach a break-even point, e.g., how many units you will have to sell to cover your warehousing cost.
How to Carry Out a Break-Even Analysis
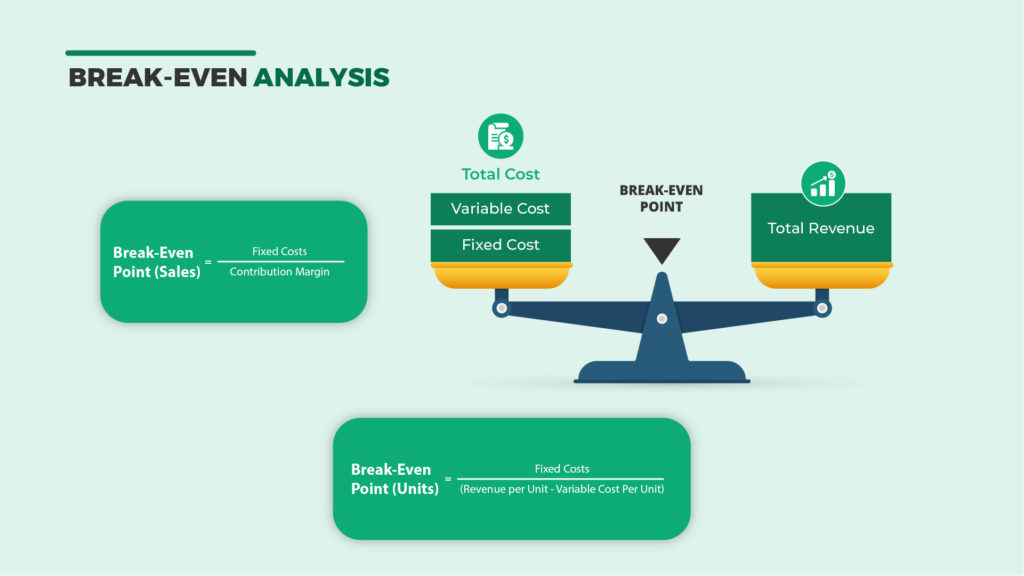
Calculating your BEP based on units is straightforward. Your break-even analysis takes fixed and variable costs into account relative to the price per unit and profit. Fixed costs refer to costs that remain the same, regardless of the units sold (such as rent and insurance), whereas variable costs refer to costs that fluctuate according to changes in sales, e.g., the cost of raw material or shipping.
To calculate your break-even point based on units, divide fixed costs by the revenue per unit minus the variable cost per unit. This can be expressed as a formula as follows:
- Break-Even Point (Units) = Fixed Costs ÷ (Revenue per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit)
To determine the break-even point based on your sales dollars, you should first determine your total variable costs and contribution margin ratio.
Total variable cost is calculated by multiplying the cost of producing one unit by the number of units you have produced, e.g. if it costs $100 to produce a single product, and you’ve produced ten units, your total variable cost will be $1,000.
The contribution margin is the difference between the price per unit and its total variable costs. In other words, if the product above sells for $150, with a variable cost of $100, the contribution margin is $50. The average variable cost is calculated by dividing your total variable costs by the number of units produced.
Now, you can conduct your break-even analysis based on sales dollars. Simply divide fixed costs by the contribution margin. The break-even formula in this would be:
- Break-Even Point (Sales) = Fixed Costs ÷ Contribution Margin
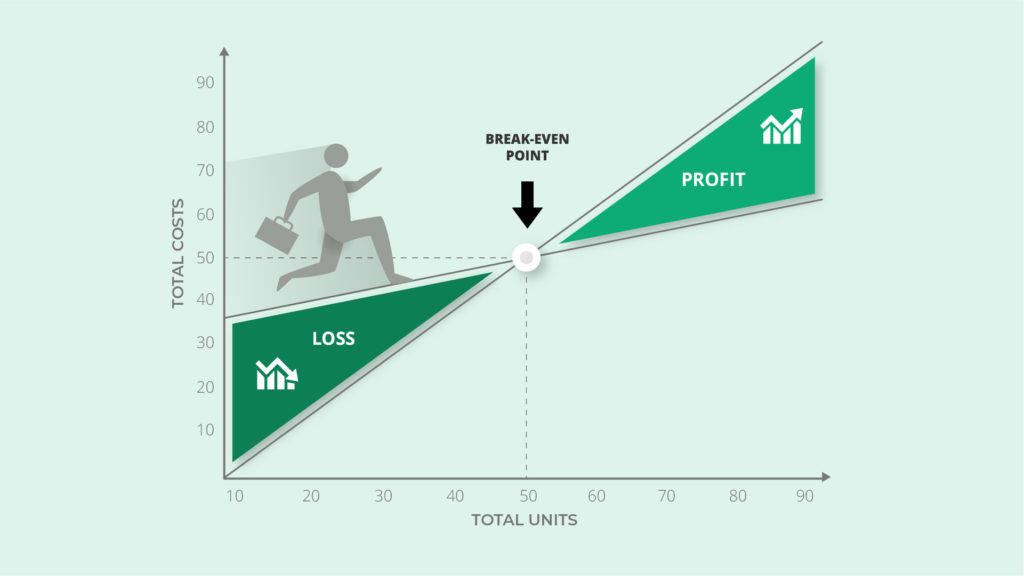
Let’s say fixed costs in this example are $20,000. With a contribution margin of $50, the break-even point in sales will be 400 units ($20,000/$40). When the company has sold 400 units, all fixed costs are complete, and there will be a net profit or loss of $0.
Once sales equal fixed and variable costs, you’ve reached your BEP. Anything over that amount is a net profit for your business, and anything under means that you’re losing money.
The Benefits of Break-Even Analysis
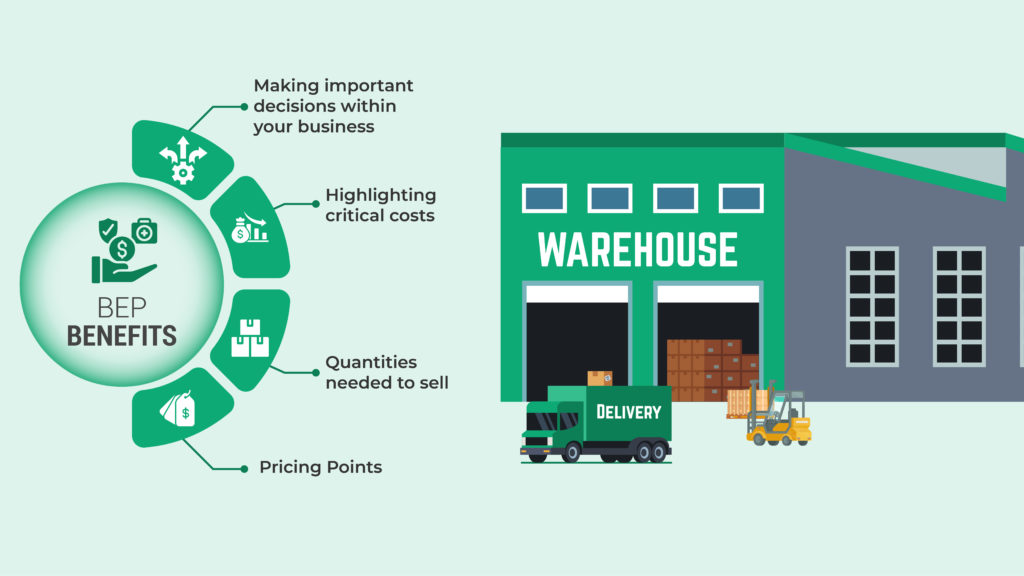
So, why do you need to know your business’s break-even point? A simple break-even calculation can provide the basis for making important decisions within your business, highlighting critical costs, quantities needed to sell, pricing points, and more.
Your break-even analysis can assist your business with:
Making Smarter Pricing Decisions
Break-even analysis determines your price per unit. That way, you can experiment with psychological pricing or promotions while remaining confident that you can cover your costs. Most businesses think about variable costs when determining their price, but a break analysis takes fixed costs into account as well so that all bases are covered.
Set Revenue Targets
Your break-even analysis will reveal how many units you’ll need to sell to become profitable. Once you know how many sales you need to make, you can set sales targets for your team accordingly.
Avoid Bad Business Ideas (and Discover Great Ones!)
Far too many businesses make decisions based on their “gut feelings.” However, it’s important to keep emotions out of the decision-making process. Conducting a break-even analysis will quickly reveal whether your business idea has the potential to make money (and how much) or whether it’s more likely to lose money.
When to Use a Break-Even Analysis
Conduct a break-even analysis whenever you add costs, either through starting a new business, merging or acquiring with another business, adding or removing products from your product mix, or expanding your staff or geographical reach. Your break-even analysis can help you understand your revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
- Before a new investment: Your break-even analysis will give your business insight into how long an investment will take to become profitable, e.g., calculating the sales required to cover the cost of expanding your office or acquiring a new warehouse.
- Before lowering pricing: Your break-even analysis will reveal whether or not a pricing strategy is feasible and how many more units you need to sell to make up for a price promotion.
- Before making decisions: There are always various what-if scenarios to consider before making a decision. Your break-even analysis tells you more about the merits of each new idea placed on the table.
Can You Influence Your Break-Even Point?
There really are only two ways to influence your break-even point: lowering your costs or raising your prices. Either way, always make sure you aren’t losing money! In addition, consider whether lowering or raising your pricing will influence your brand or market in other potentially harmful ways. This includes damaging your reputation, increasing churn, or lowering the quality of your product (which has its own repercussions).
As part of break-even analysis, an ERP system provides insight and information across product lines, business groups, and geographic locations. It helps reveal more about your business and financial status than a break-even analysis may be able to do on its own.
If you’d like to know more about the various elements at work in your business, speak with us at 10X ERP. We’re also here to help your efforts in conducting a break-even analysis on your ERP options! We love to see you succeed, whether it’s through a new idea or expanding on an existing one.
