Overview
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a critical software solution that integrates various business functions to enhance operational efficiency and decision-making. Understanding its significance is paramount for modern organizations. ERP streamlines processes, improves return on investment (ROI) by an impressive 30% within three years, and facilitates real-time data access. These elements collectively underscore the necessity of ERP for organizations striving for a competitive advantage. As Operations Managers, recognizing the transformative potential of ERP can lead to more informed decisions and strategic improvements.
Introduction
The realm of business management is rapidly evolving, and at the heart of this transformation lies a powerful tool known as Enterprise Resource Planning, or ERP. This sophisticated software solution is not merely a trend; it is a cornerstone for organizations striving to enhance operational efficiency and streamline their processes. As companies increasingly recognize the necessity of integrated systems to optimize their operations, a pressing question arises: how can businesses leverage ERP to not only survive but thrive in a competitive landscape? Exploring the full potential of ERP reveals its critical importance and transformative features that can redefine success for modern enterprises.
Define ERP: Full Form and Core Concept
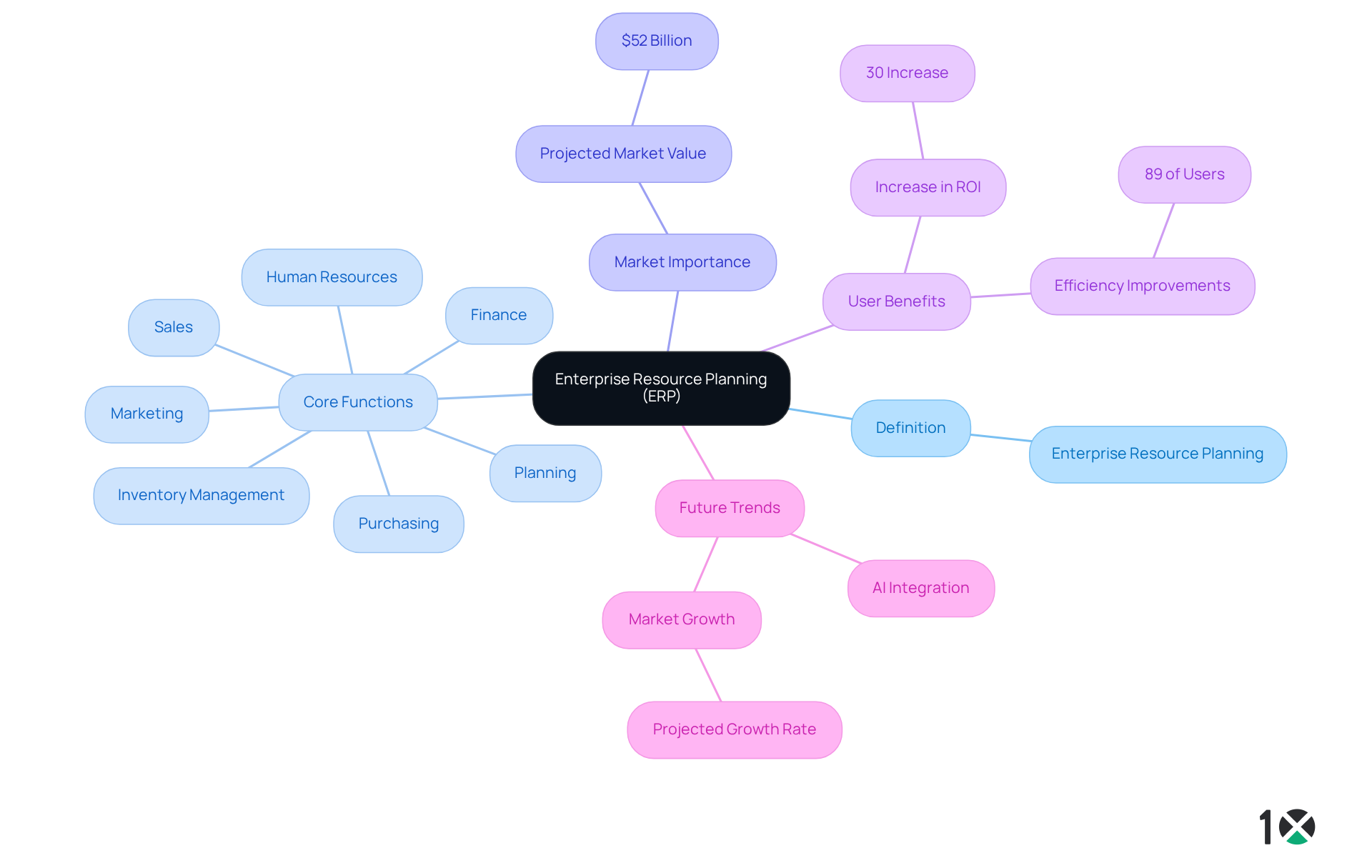
The ERP full form, which is Enterprise Resource Planning, refers to a sophisticated software solution that organizations use to manage and integrate critical business functions. By unifying planning, purchasing, inventory management, sales, marketing, finance, and human resources into a cohesive framework, ERP significantly enhances operational efficiency and fosters seamless information sharing across departments. This integration is crucial for bolstering decision-making capabilities and streamlining processes.
As we approach 2025, the importance of ERP solutions, known by the ERP full form as Enterprise Resource Planning, continues to escalate, with the global ERP market projected to exceed $52 billion. Companies increasingly recognize the necessity for integrated solutions to optimize their operations, with 89% of users identifying efficiency improvements as a primary advantage. Furthermore, organizations that implement ERP solutions report a remarkable 30% increase in ROI within three years, underscoring the financial benefits of adopting such technology.
Real-world examples underscore the transformative effects of ERP integration. For instance, manufacturers account for 47% of ERP software purchasers, driven by the demand for enhanced functionality and operational efficiency. Additionally, 91% of organizations that have embraced ERP systems have reported optimized inventory levels, illustrating the tangible benefits of these solutions.
Expert perspectives highlight that the ERP full form transcends mere software; it serves as a strategic resource that facilitates comprehensive organizational management. As financial leaders prioritize advancements in ERP technology, the integration of AI and machine learning is anticipated to elevate operational efficiency by up to 40%. This evolution reflects the growing recognition of ERP’s pivotal role in steering organizational success and adapting to the complexities of modern markets.
Trace the Evolution of ERP: History and Development
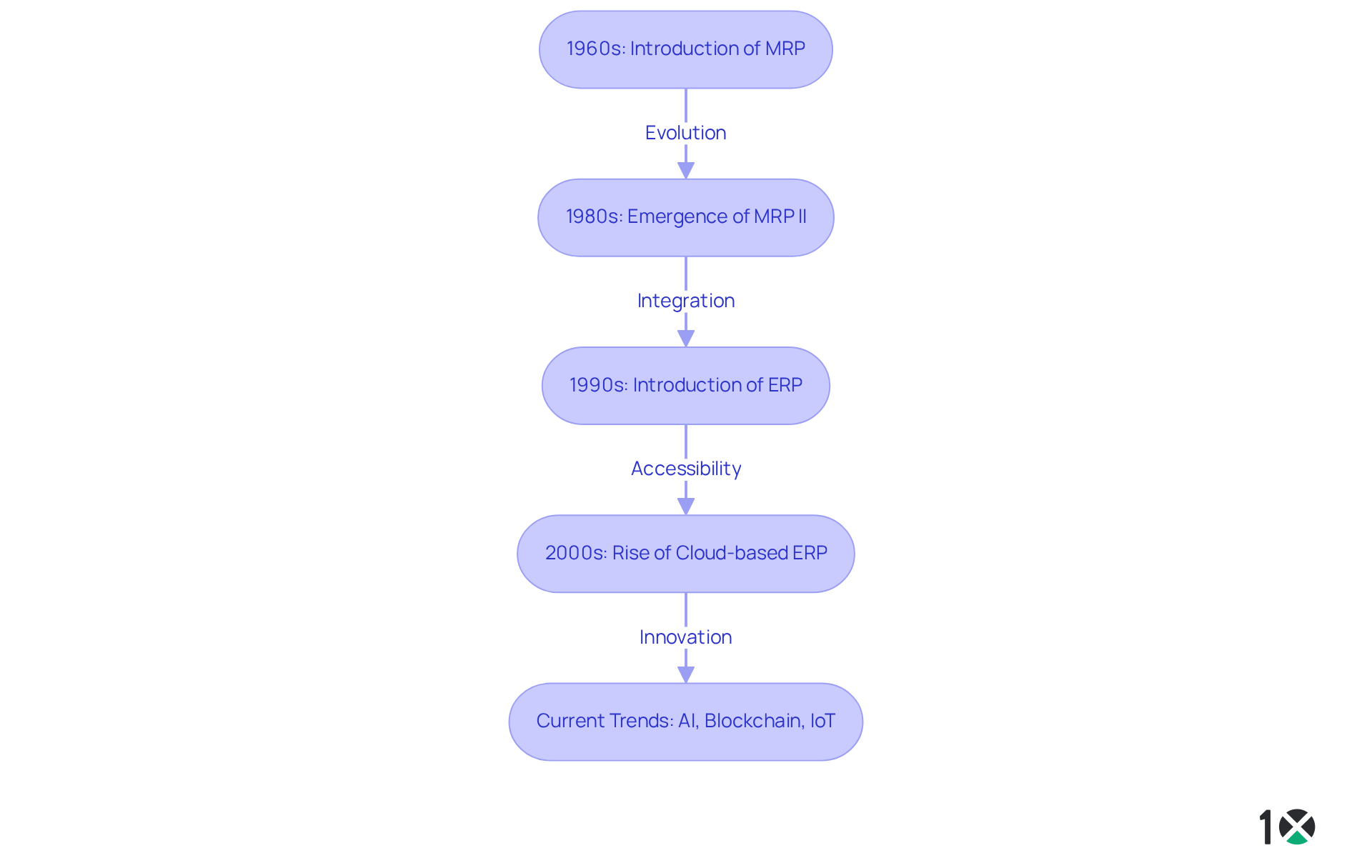
The roots of ERP can be traced back to the 1960s with the introduction of Material Requirements Planning (MRP) frameworks, which primarily focused on overseeing manufacturing processes. As companies grew and technology advanced, the limitations of MRP became evident, leading to the development of more integrated solutions. By the 1980s, MRP II emerged, incorporating additional functionalities such as quality control and financial management. The ERP full form, which stands for ‘Enterprise Resource Planning’, was formally introduced in the 1990s, marking a significant transition towards software that could integrate various business functions into a unified framework.
The evolution continued into the 2000s with the rise of cloud-based ERP solutions, revolutionizing accessibility and collaboration. Contemporary ERP solutions leverage advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, facilitating real-time data insights and automation. Notably, 10X ERP stands out with its best-in-class accounting, unlimited integrations, and robust data integrity and security features. Statistics reveal that:
- 68% of organizations report revenue growth due to cloud-based ERP platforms.
- 63% observe a decrease in operational costs.
This shift from conventional on-site technologies to cloud solutions has made ERP more attainable for organizations of all sizes, promoting enhanced operational efficiency and decision-making across departments.
Currently, ERP platforms, particularly comprehensive solutions like 10X ERP, are essential for organizations aiming to optimize operations and improve their competitive edge in an ever-evolving market. Emerging trends such as AI, blockchain, and IoT are shaping the future of ERP, underscoring the necessity for organizations to select the right ERP partner to maximize their investment and ensure long-term success.
Examine Key Features of ERP Systems: Components and Functionalities
Key features of ERP systems include:
-
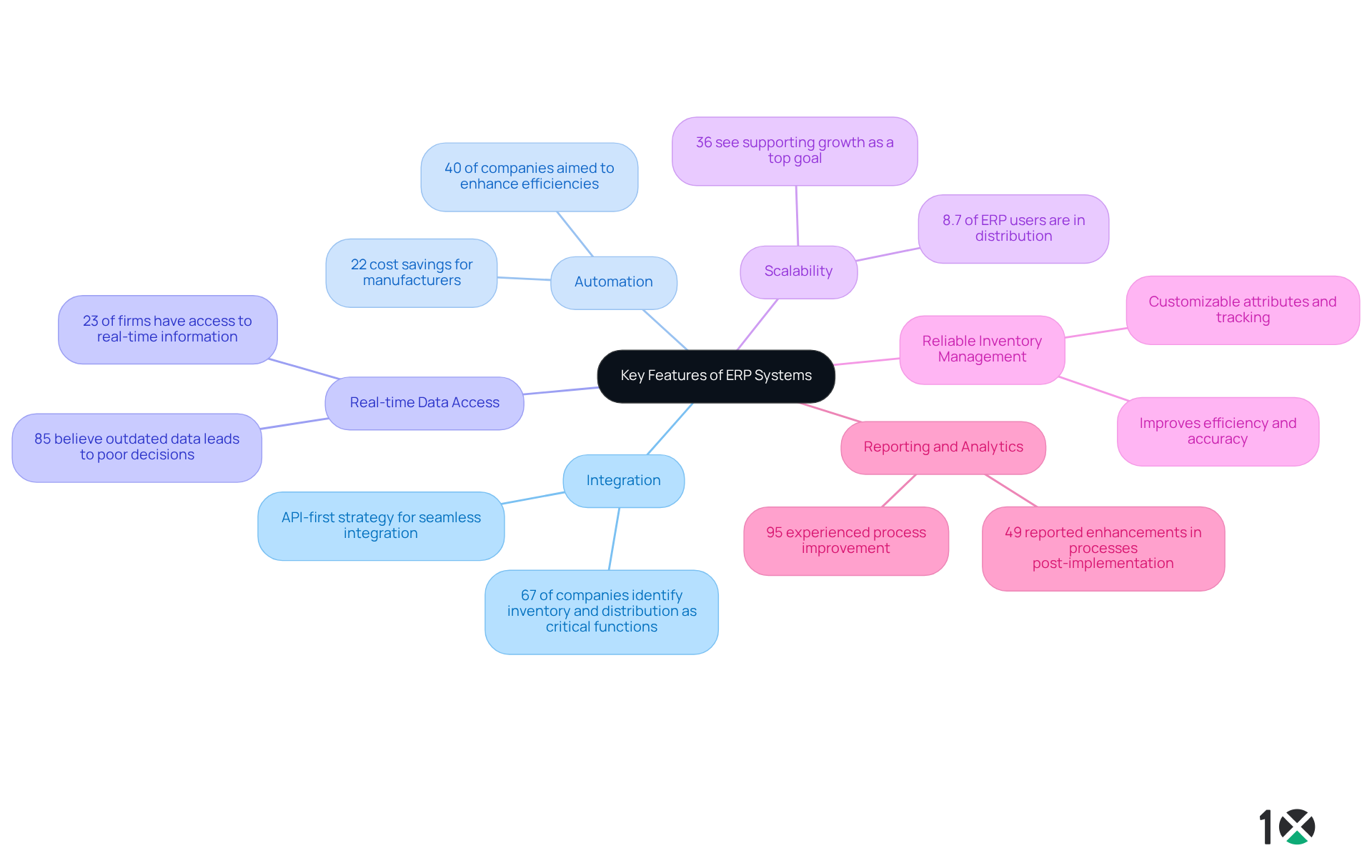
Integration: ERP systems seamlessly connect various business processes, facilitating smooth data flow across departments. This integration is crucial, as 67% of companies identify inventory and distribution as critical functions of the ERP full form, while 21% recognize technology as vital, underscoring the need for cohesive operations. With 10X ERP’s API-first strategy, organizations can achieve seamless integration with nearly any software they currently utilize or may adopt in the future.
-
Automation: Routine tasks such as order processing, invoicing, and reporting can be automated, significantly reducing manual effort and minimizing errors. Statistics indicate that the ERP full form solutions can save manufacturers as much as 22% in expenses, and 40% of companies aimed to enhance efficiencies in transactions with ERP, emphasizing the wider influence of automation beyond merely cost reductions.
-
Real-time Data Access: Users benefit from immediate access to up-to-date information, which empowers informed decision-making. Currently, just 23% of firms have access to real-time information, and 85% believe that outdated data, which relates to the ERP full form, results in poor decision-making, suggesting a significant opportunity for enhancement in operational efficiency. 10X ERP provides real-time data processing, ensuring that distributors can make timely and informed decisions.
-
Scalability: ERP solutions are designed to expand in tandem with organizations, handling rising data quantities and user requirements. This scalability is essential for distributors, as 8.7% of companies using ERP systems, with the ERP full form being Enterprise Resource Planning, are in distribution, and 36% see supporting growth as a top goal for ERP, necessitating adaptable solutions. 10X ERP’s scalable architecture accommodates the changing requirements of distribution enterprises.
-
Reliable Inventory Management: 10X ERP offers simplified item types, customizable attributes, and powerful cross-referencing, along with lot and serial item tracking. This guarantees companies understand precisely where their inventory is at any moment, improving efficiency and accuracy.
-
Reporting and Analytics: Advanced reporting tools offer valuable insights into organizational performance, enabling entities to identify trends and make strategic decisions. Significantly, 49% of firms reported enhancements in all processes after implementation, and 95% experienced process improvement following ERP implementation, emphasizing that understanding the ERP full form is crucial for driving success with strong analytics. With 10X ERP, distributors can utilize powerful analytics to enhance their business strategies.
Understand the Importance of ERP in Business Operations
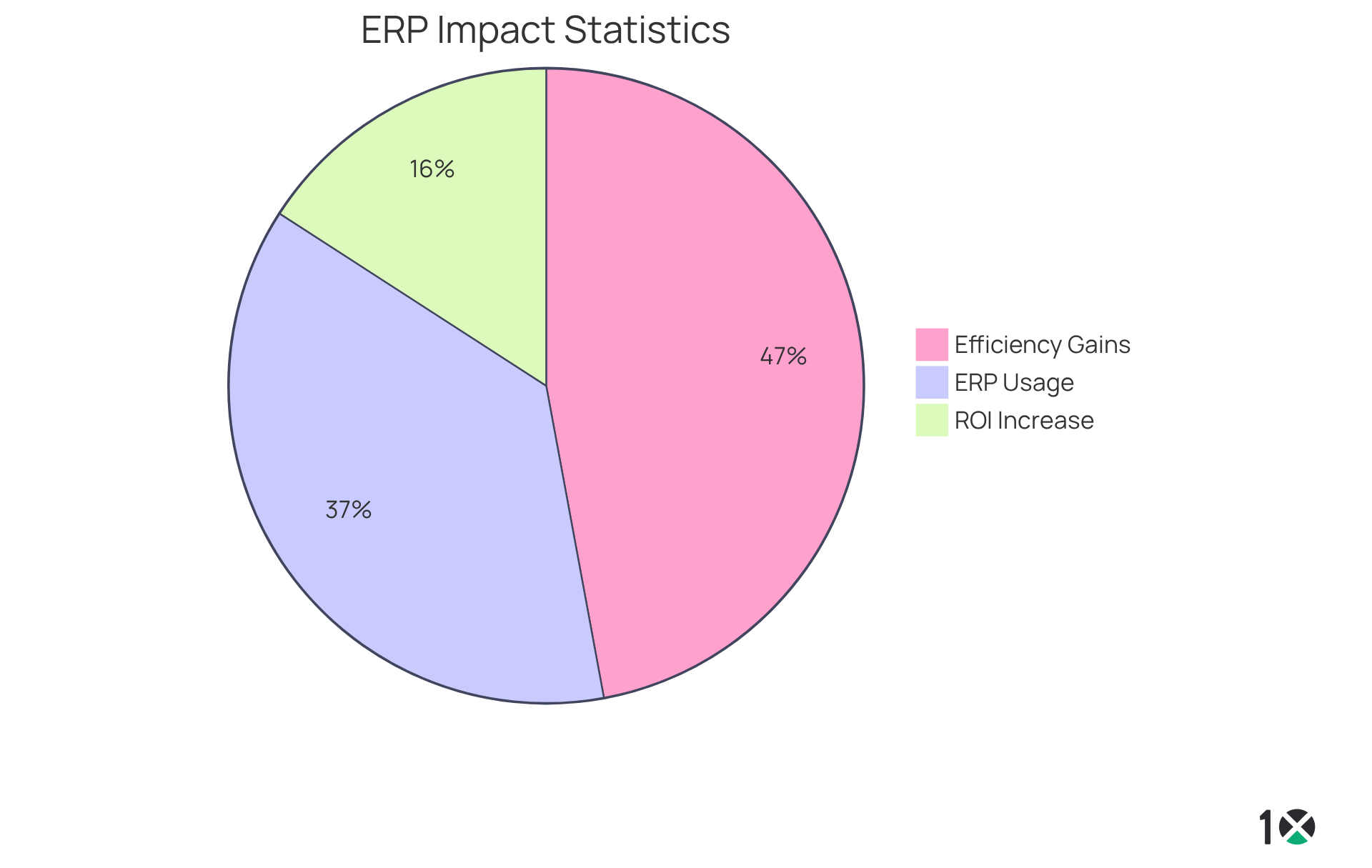
The ERP full form illustrates that ERP solutions are essential for modern enterprises, significantly optimizing operations and enhancing efficiency. By centralizing data and automating core processes, organizations can achieve substantial reductions in operational costs while improving overall productivity. Companies that have implemented ERP solutions have reported an impressive 30% increase in return on investment within three years. Furthermore, ERP solutions foster enhanced cooperation among departments by ensuring that all teams access the same real-time information. This unified approach not only improves decision-making but also elevates customer service by delivering timely and accurate data.
In a competitive environment, the ability to react quickly to market shifts and customer needs is vital. Thus, understanding the ERP full form is crucial as these solutions emerge as a vital resource for achieving success. With 70% of large enterprises utilizing ERP technology, the impact on productivity improvement is clear, as organizations experience efficiency gains of up to 89%. As businesses continue to evolve, integrating ERP systems, which have an ERP full form of Enterprise Resource Planning, will remain a key driver of operational excellence, underscoring the necessity for Operations Managers to consider these solutions seriously.
Conclusion
The concept of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) encapsulates a vital framework that modern organizations leverage to enhance operational efficiency and streamline critical business functions. By integrating various processes such as finance, inventory management, and human resources, ERP systems serve as a backbone for informed decision-making and improved collaboration across departments. As the global market for ERP solutions continues to expand, understanding its full form and significance becomes increasingly essential for businesses aiming to thrive in a competitive landscape.
Key insights throughout this discussion have highlighted the transformative power of ERP systems. Their historical evolution, starting with Material Requirements Planning (MRP) to today’s advanced cloud-based solutions, demonstrates how ERP has consistently adapted to meet the changing demands of businesses. Features such as automation, real-time data access, and robust reporting capabilities drive efficiency and productivity. Furthermore, the substantial return on investment reported by organizations adopting ERP underscores its critical role in achieving operational excellence.
Ultimately, the importance of ERP in modern business operations cannot be overstated. As organizations face the challenges of rapid market changes and increased customer expectations, investing in ERP solutions emerges as a strategic imperative. Embracing this technology not only facilitates better resource management but also positions companies to respond swiftly to evolving demands, ensuring long-term success and sustainability in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does ERP stand for?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning.
What is the core concept of ERP?
The core concept of ERP is a sophisticated software solution that organizations use to manage and integrate critical business functions such as planning, purchasing, inventory management, sales, marketing, finance, and human resources into a cohesive framework.
How does ERP enhance operational efficiency?
ERP enhances operational efficiency by unifying various business functions, which fosters seamless information sharing across departments and bolsters decision-making capabilities.
What is the projected growth of the ERP market by 2025?
The global ERP market is projected to exceed $52 billion by 2025.
What percentage of ERP users identify efficiency improvements as a primary advantage?
89% of ERP users identify efficiency improvements as a primary advantage.
What financial benefits do organizations experience after implementing ERP solutions?
Organizations that implement ERP solutions report a remarkable 30% increase in ROI within three years.
Which sector accounts for the largest percentage of ERP software purchasers?
Manufacturers account for 47% of ERP software purchasers.
What inventory-related benefit do organizations report after adopting ERP systems?
91% of organizations that have embraced ERP systems have reported optimized inventory levels.
How is ERP viewed beyond just software?
ERP is viewed as a strategic resource that facilitates comprehensive organizational management.
What advancements in ERP technology are financial leaders prioritizing?
Financial leaders are prioritizing advancements in ERP technology, particularly the integration of AI and machine learning, which is anticipated to elevate operational efficiency by up to 40%.
